脱产备考ACCA?这些备考建议我不允许你没看过!
发布时间:2020-03-12
ACCA考试共有16门科目,包括12门必修以及四门选修。数量众多的考试科目,让一些志在ACCA会员的小伙伴选择了脱产备考。而如何脱产备考ACCA最有效,就是这些小伙伴关心的问题。鉴于此,51题库考试学习网在下面为大家带来ACCA备考学习计划的相关信息,以供参考。
在制定学习计划时,我们首先要有一个大概的粗框架。根据考试内容来看,ACCA每门科目大约需要150-200小时准备。当然了,每个科目具体时间的长短取决于课程本身的难易以及考生原先对这方面知识的了解程度以及时间安排的效率等诸多因素。因此,这个时间仅供参考。考生在备考时,如果每周看书做题20-25小时,同时准备三门课要大约20周的时间。因此,小伙伴们如果觉得时间不够,就不要好高骛远,一次考两门为佳。毕竟,ACCA考试费不低。
除了从考试内容来制定学习计划外,我们还可以通过教材内容制定学习计划。当你完成了ACCA考试报名并购书后,根据书的厚度,练习题量的多少,安排一个切实的学习计划。注意,小伙伴们在制定学习计划时一定要细化,不能太过笼统,比如说,“我要1个月内看完三本书”。先要看一下你自己的阅读速度,10page每小时大概是一个比较实际的速度。不同的人阅读速度不同,小伙伴们要根据自己的实际情况进行合理地调整。
除了教材学习之外,小伙伴们也应该去做一些练习题。在做题时,我们应该看一下练习题有多少题,估算一下练习时间。同时,每道题都有分值的,如果考试的时候,10分值的题目只能分配18分钟时间。如果花费的时间较多,很可能导致考试的时候时间不够用。作为练习,时间可以多一些,因为除了做题,你还要分析答案。因此,在日常练习时,10分值的题可以是大约用25-30分钟,一道20-30分值的中型题,最少要一个小时。小伙伴们在日常练习时,也要注意不断提升自己的做题速度哦。
除了做练习题,做ACCA全真试题也是很重要的。有不少题目被直接拷贝到练习题中(Authorized Reproduce),也有些题目是被做过略微修改。这些题目都能够在ACCA官网上面获得,具体获得途径还需要小伙伴们咨询ACCA官方。
一般来说,做全真题的目的首先是让大家熟悉每年ACCA考官出题的风格以及大致的一个答题思路,其次是让大家在真正的时间压力下感受一下考试的感觉,考验一下你答题,尤其是写字的速度。毕竟ACCA考试的F阶段均为机考,全英文答题模式比较耗时间。另外需要注意的一点是,小伙伴们做真题时,数量不能太少,最少完整地做两三套全真题。
以上就是关于ACCA学习计划的相关情况。51题库考试学习网提醒:不同的人适用的学习方法不同,小伙伴们在使用以上学习方法时要根据自己的实际情况进行适当调整哦。最后,51题库考试学习网预祝准备参加2020年ACCA考试的小伙伴都能顺利通过。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
18 Which of the following statements about accounting ratios and their interpretation are correct?
1 A low-geared company is more able to survive a downturn in profit than a highly-geared company.
2 If a company has a high price earnings ratio, this will often indicate that the market expects its profits to rise.
3 All companies should try to achieve a current ratio (current assets/current liabilities) of 2:1.
A 2 and 3 only
B 1 and 3 only
C 1 and 2 only
D All three statements are correct
(ii) Analyse the effect of delaying the sale of the business of the Stiletto Partnership to Razor Ltd until
30 April 2007 on Clint’s income tax and national insurance position.
You are not required to prepare detailed calculations of his income tax or national insurance liabilities.
(4 marks)
(ii) The implications of delaying the sale of the business
The implications of delaying the sale of the business until 30 April would have been as follows:
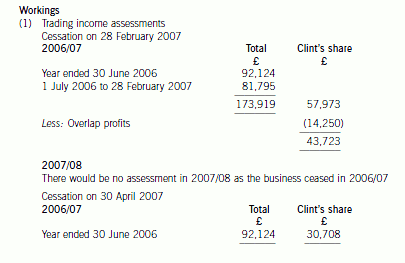
– Clint would have received an additional two months of profits amounting to £6,920 (£20,760 x 1/3).
– Clint’s trading income in 2006/07 would have been reduced by £13,015 (£43,723 – £30,708), much of which
would have been subject to income tax at 40%. His additional trading income in 2007/08 of £19,935 would all
have been taxed at 10% and 22%.
– Clint is entitled to the personal age allowance of £7,280 in both years. However, it is abated by £1 for every £2
by which his total income exceeds £20,100. Once Clint’s total income exceeds £24,590 (£20,100 + ((£7,280
– £5,035) x 2)), his personal allowance will be reduced to the standard amount of £5,035. Accordingly, the
increased personal allowance would not be available in 2006/07 regardless of the year in which the business was
sold. It is available in 2007/08 (although part of it is wasted) but would not have been if the sale of the business
had been delayed.
– Clint’s class 4 national insurance contributions in 2006/07 would have been reduced due to the fall in the level
of his trading income. However, much of the saving would be at 1% only. Clint is not liable to class 4 national
insurance contributions in 2007/08 as he is 65 at the start of the year.
– Changing the date on which the business was sold would have had no effect on Clint’s class 2 liability as he is
not required to make class 2 contributions once he is 65 years old.
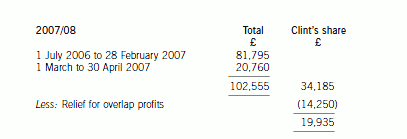
(b) Identify and explain the financial statement risks to be taken into account in planning the final audit.
(12 marks)
(b) Financial statement risks
Tutorial note: Note the timeframe. Financial statements for the year to 30 June 2006 are draft. Certain misstatements
may therefore exist due to year-end procedures not yet having taken place.
Revenue/(Receivables)
■ Revenue has increased by 11·8% ((161·5 – 144·4)/144·4 × 100). Overstatement could arise if rebates due to customers
have not yet been accounted for in full (as they are calculated in arrears). If rebates have still to be accounted for trade
receivables will be similarly overstated.
Materials expense
■ Materials expense has increased by 17·8% ((88.0 – 74·7)/74·7 × 100). This is more than the increase in revenue. This
could be legitimate (e.g. if fuel costs have increased significantly). However, the increase could indicate misclassification
of:
– revenue expenditure (see fall in other expenses below);
– capital expenditure (e.g. on overhauls or major refurbishment) as revenue;
– finance lease payments as operating lease.
Depreciation/amortisation
■ This has fallen by 10·5% ((8·5 – 9·5)/9·5 × 100). This could be valid (e.g. if Yates has significant assets already fully
depreciated or the asset base is lower since last year’s restructuring). However, there is a risk of understatement if, for
example:
– not all assets have been depreciated (or depreciated at the wrong rates, or only for 11 months of the year);
– cost of non-current assets is understated (e.g. due to failure to recognise capital expenditure)1;
– impairment losses have not been recognised (as compared with the prior year).
Tutorial note: Depreciation on vehicles and transport equipment represents only 7% of cost. If all items were being
depreciated on a straight-line basis over eight years this should be 12·5%. The depreciation on other equipment looks more
reasonable as it amounts to 14% which would be consistent with an average age of vehicles of seven years (i.e. in the middle
of the range 3 – 13 years).
Other expenses
■ These have fallen by 15·5% ((19·6 – 23·2)/23·2 × 100). They may have fallen (e.g. following the restructuring) or may be
understated due to:
– expenses being misclassified as materials expense;
– underestimation of accrued expenses (especially as the financial reporting period has not yet expired).
Intangibles
■ Intangible assets have increased by $1m (16% on the prior year). Although this may only just be material to the
financial statements as a whole (see (a)) this is the net movement, therefore additions could be material.
■ Internally-generated intangibles will be overstated if:
– any of the IAS 38 recognition criteria cannot be demonstrated;
– any impairment in the year has not yet been written off in accordance with IAS 36 ‘Impairment of Assets’.
Tangible assets
■ The net book value of property (at cost) has fallen by 5%, vehicles are virtually unchanged (increased by just 2·5%)
and other equipment (though the least material category) has fallen by 20·4%.
■ Vehicles and equipment may be overstated if:
– disposals have not been recorded;
– depreciation has been undercharged (e.g. not for a whole year);
– impairments have not yet been accounted for.
■ Understatement will arise if finance leases are treated as operating leases.
Receivables
■ Trade receivables have increased by just 2·2% (although sales increased by 11·8%) and may be understated due to a
cutoff error resulting in overstatement of cash receipts.
■ There is a risk of overstatement if sufficient allowances have not been made for the impairment of individually significant
balances and for the remainder assessed on a portfolio or group basis.
Restructuring provision
■ The restructuring provision that was made last year has fallen/been utilised by 10·2%. There is a risk of overstatement
if the provision is underutilised/not needed for the purpose for which it was established.
Finance lease liabilities
■ Although finance lease liabilities have increased (by $1m) there is a greater risk of understatement than overstatement
if leased assets are not recognised on the balance sheet (i.e. capitalised).
■ Disclosure risk arises if the requirements of IAS 17 ‘Leases’ (e.g. in respect of minimum lease payments) are not met.
Trade payables
■ These have increased by only 5·3% compared with the 17·8% increase in materials expense. There is a risk of
understatement as notifications (e.g. suppliers’ invoices) of liabilities outstanding at 30 June 2006 may have still to be
received (the month of June being an unexpired period).
Other (employee) liabilities
■ These may be understated as they have increased by only 7·5% although staff costs have increased by 14%. For
example, balances owing in respect of outstanding holiday entitlements at the year end may not yet be accurately
estimated.
Tutorial note: Credit will be given to other financial statements risks specific to the scenario. For example, ‘time-sensitive
delivery schedules’ might give rise to penalties or claims, that could result in understated provisions or undisclosed
contingent liabilities. Also, given that this is a new audit and the result has changed significantly (from loss to profit) might
suggest a risk of misstatement in the opening balances (and hence comparative information).
1 Tutorial note: This may be unlikely as other expenses have fallen also.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-02-05
- 2020-04-09
- 2020-03-11
- 2019-03-28
- 2020-03-20
- 2020-04-14
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-02-28
- 2020-01-09
- 2021-04-23
- 2019-12-28
- 2019-12-29
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-11
- 2020-03-22
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-04-15
- 2020-04-03
- 2020-02-19
- 2020-03-11
- 2020-03-21
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-14
- 2020-01-09
- 2021-05-14
- 2020-03-08