看过来!ACCA2020年中国区考点查询
发布时间:2020-03-19
小伙伴们注意了,关于ACCA2020年中国区考点查询,不知道赶紧跟着51题库考试学习网一起来了解一下吧!
ACCA在国内的考点可以通过下方进行查询,如果还有其他问题,可在线咨询51题库考试学习网。



以上就是51题库考试学习网带给大家的内容,如果还有其他不清楚的问题,请及时反馈给51题库考试学习网,我们会尽快帮您解答。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
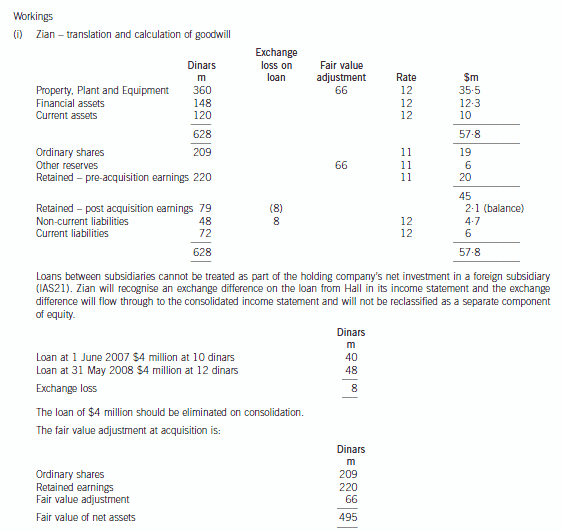
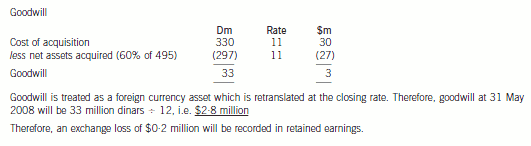
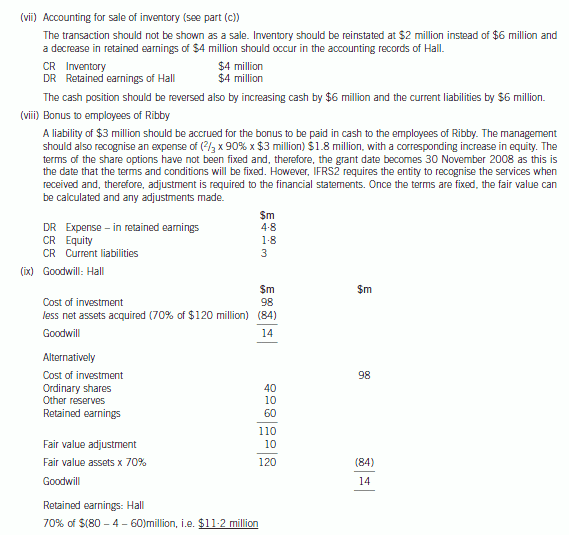
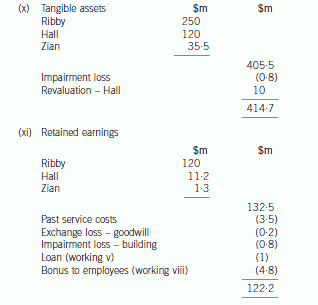
(b) Prepare a consolidated statement of financial position of the Ribby Group at 31 May 2008 in accordance
with International Financial Reporting Standards. (35 marks)




(d) Draft a letter for Tim Blake to send to WM’s investors to include the following:
(i) why you believe robust internal controls to be important; and
(ii) proposals on how internal systems might be improved in the light of the overestimation of mallerite at
WM.
Note: four professional marks are available within the marks allocated to requirement (d) for the structure,
content, style. and layout of the letter.
(16 marks)

You will be aware of the importance of accurate resource valuation to Worldwide Minerals (WM). Unfortunately, I have to
inform. you that the reserve of mallerite, one of our key minerals in a new area of exploration, was found to have been
overestimated after the purchase of a mine. It has been suggested that this information may have an effect on shareholder
value and so I thought it appropriate to write to inform. you of how the board intends to respond to the situation.
In particular, I would like to address two issues. It has been suggested that the overestimation arose because of issues with
the internal control systems at WM. I would firstly like to reassure you of the importance that your board places on sound
internal control systems and then I would like to highlight improvements to internal controls that we shall be implementing
to ensure that the problem should not recur.
(i) Importance of internal control
Internal control systems are essential in all public companies and Worldwide Minerals (WM) is no exception. If anything,
WM’s strategic position makes internal control even more important, operating as it does in many international situations
and dealing with minerals that must be guaranteed in terms of volume, grade and quality. Accordingly, your board
recognises that internal control underpins investor confidence. Investors have traditionally trusted WM’s management
because they have assumed it capable of managing its internal operations. This has, specifically, meant becoming aware
of and controlling known risks. Risks would not be known about and managed without adequate internal control
systems. Internal control, furthermore, helps to manage quality throughout the organisation and it provides
management with information on internal operations and compliance. These features are important in ensuring quality
at all stages in the WM value chain from the extraction of minerals to the delivery of product to our customers. Linked
to this is the importance of internal control in helping to expose and improve underperforming internal operations.
Finally, internal control systems are essential in providing information for internal and external reporting upon which, in
turn, investor confidence rests.
(ii) Proposals to improve internal systems at WM
As you may be aware, mineral estimation and measurement can be problematic, particularly in some regions. Indeed,
there are several factors that can lead to under or overestimation of reserves valuations as a result of geological survey
techniques and regional cultural/social factors. In the case of mallerite, however, the issues that have been brought to
the board’s attention are matters of internal control and it is to these that I would now like to turn.
In first instance, it is clear from the fact that the overestimate was made that we will need to audit geological reports at
an appropriate (and probably lower) level in the organisation in future.
Once a claim has been made about a given mineral resource level, especially one upon which investor returns might
depend, appropriate systems will be instituted to ask for and obtain evidence that such reserves have been correctly and
accurately quantified.
We will recognise that single and verbal source reports of reserve quantities may not necessarily be accurate. This was
one of the apparent causes of the overestimation of mallerite. A system of auditing actual reserves rather than relying
on verbal evidence will rectify this.
The purchase of any going concern business, such as the mallerite mine, is subject to due diligence. WM will be
examining its procedures in this area to ensure that they are fit for purpose in the way that they may not have been in
respect of the purchase of the mallerite mine. I will be taking all appropriate steps to ensure that all of these internal
control issues can be addressed in future.
Thank you for your continued support of Worldwide Minerals and I hope the foregoing goes some way to reassure you
that the company places the highest value on its investors and their loyalty.
Yours faithfully,
Tim Blake
Chairman
(b) Using the information contained in Appendix 1.1, discuss the financial performance of HLP and MAS,
incorporating details of the following in your discussion:
(i) Overall client fees (total and per consultation)
(ii) Advisory protection scheme consultation ‘utilisation levels’ for both property and commercial clients
(iii) Cost/expense levels. (10 marks)
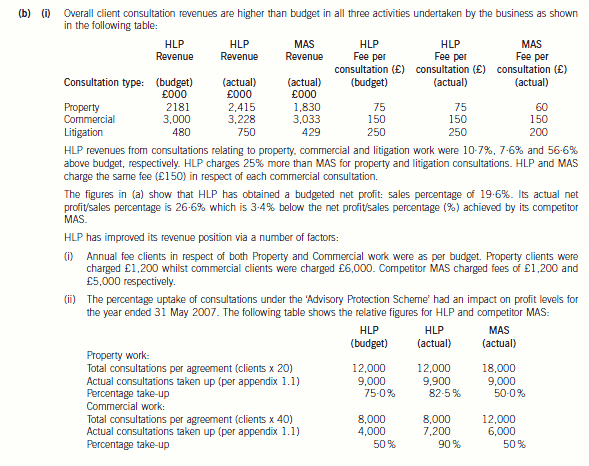
(ii) As far as annual agreements relating to property work are concerned, HLP had a take up rate of 82·5% whereas MAS
had a take up rate of only 50%. Therefore, HLP has ‘lost out’ to competitor MAS in relative financial terms as regards
the ‘take-up’ of consultations relating to property work. This is because both HLP and MAS received an annual fee from
each property client irrespective of the number of consultations given. MAS should therefore have had a better profit
margin from this area of business than HLP. However, the extent to which HLP has ‘lost out’ cannot be quantified since
we would need to know the variable costs per consultation and this detail is not available. What we do know is that
HLP earned actual revenue per effective consultation amounting to £90·90 whereas the budgeted revenue per
consultation amounted to £100. MAS earned £120 per effective consultation.
The same picture emerges from annual agreements relating to commercial work. HLP had a budgeted take up rate of
50%, however the actual take up rate during the period was 90%. MAS had an actual take up rate of 50%. The actual
revenue per effective consultation earned by HLP amounted to £167 whereas the budgeted revenue per consultation
amounted to £300. MAS earned £250 per effective consultation.
There could possibly be an upside to this situation for HLP in that it might be the case that the uptake of 90% of
consultations without further charge by clients holding annual agreements in respect of commercial work might be
indicative of a high level of customer satisfaction. It could on the other hand be indicative of a mindset which says ‘I
have already paid for these consultations therefore I am going to request them’.
(iii) Budgeted and actual salaries in HLP were £50,000 per annum, per advisor. Two additional advisors were employed
during the year in order to provide consultations in respect of commercial work. MAS paid a salary of £60,000 to each
advisor which is 20% higher than the salary of £50,000 paid to each advisor by HLP. Perhaps this is indicative that
the advisors employed by MAS are more experienced and/or better qualified than those employed by HLP.
HLP paid indemnity insurance of £250,000 which is £150,000 (150%) more than the amount of £100,000 paid by
MAS. This excess cost may well have arisen as a consequence of successful claims against HLP for negligence in
undertaking commercial work. It would be interesting to know whether HLP had been the subject of any successful
claims for negligent work during recent years as premiums invariably reflect the claims history of a business. Rather
worrying is the fact that HLP was subject to three such claims during the year ended 31 May 2007.
Significant subcontract costs were incurred by HLP during the year probably in an attempt to satisfy demand and retain
the goodwill of its clients. HLP incurred subcontract costs in respect of commercial properties which totalled £144,000.
These consultations earned revenue amounting to (320 x £150) = £48,000, hence a loss of £96,000 was incurred
in this area of the business.
HLP also paid £300,000 for 600 subcontract consultations in respect of litigation work. These consultations earned
revenue amounting to (600 x £250) = £150,000, hence a loss of £150,000 was incurred in this area of the business.
In contrast, MAS paid £7,000 for 20 subcontract consultations in respect of commercial work and an identical amount
for 20 subcontract consultations in respect of litigation work. These consultations earned revenue amounting to
20 x (£150 + £200) =£7,000. Therefore, a loss of only £7,000 was incurred in respect of subcontract consultations
by MAS.
Other operating expenses were budgeted at 53·0% of sales revenue. The actual level incurred was 40·7% of sales
revenue. The fixed/variable split of such costs is not given but it may well be the case that the fall in this percentage is
due to good cost control by HLP. However, it might simply be the case that the original budget was flawed. Competitor
MAS would appear to have a slightly superior cost structure to that of HLP since its other operating expenses amounted
to 38·4% of sales revenue. Further information is required in order to draw firmer conclusions regarding cost control
within both businesses.
(ii) Discuss TWO problems that may be faced in implementing quality control procedures in a small firm of
Chartered Certified Accountants, and recommend how these problems may be overcome. (4 marks)
(ii) Consultation – it may not be possible to hold extensive consultations on specialist issues within a small firm, due to a
lack of specialist professionals. There may be a lack of suitably experienced peers to discuss issues arising on client
engagements. Arrangements with other practices for consultation may be necessary.
Training/Continuing Professional Development (CPD) – resources may not be available, and it is expensive to establish
an in-house training function. External training consortia can be used to provide training/CPD for qualified staff, and
training on non-exam related issues for non-qualified staff.
Review procedures – it may not be possible to hold an independent review of an engagement within the firm due to the
small number of senior and experienced auditors. In this case an external review service may be purchased.
Lack of specialist experience – where special skills are needed within an engagement; the skills may be bought in, for
example, by seconding staff from another practice. Alternatively if work is too specialised for the firm, the work could be
sub-contracted to another practice.
Working papers – the firm may lack resources to establish an in-house set of audit manuals or standard working papers.
In this case documentation can be provided by external firms or professional bodies.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-02-28
- 2020-02-05
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-03-22
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-03-05
- 2020-03-20
- 2020-04-17
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-04
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-28
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-30
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-12-28
- 2020-02-29
- 2020-04-16
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-03
- 2020-03-11
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-04
- 2020-03-29
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-05-16
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-03-20
- 2021-04-23