考生必看,7月份ACCA考试最新公告!
发布时间:2020-05-12
随着7月份ACCA考试的到来,很多小伙伴咨询ACCA考试相关的最新公告,今天51题库考试学习网为大家来分享。
一、在校学员所需准备的注册资料
(1)中英文在读证明(由学校教务部门开具,加盖公章,在读证明及成绩单加盖的公章必须一致)
(2)中英文在校期间各年级成绩单(至少要提供大一成绩单,并加盖所在学校或学校教务部门公章)
(3)中英文个人身份证件或护照
(4)2寸彩色证件照一张
(5)注册报名费(现金代缴或信用卡支付)
二、非在校学员所需准备的注册资料(原件、复印件和译文)
(1)中英文个人身份证件或护照
(2)中英文学历证明(毕业证及学位证)
(3)2寸彩色证件照一张
三、不具备以上条件,可通过FIA途径注册ACCA
(1)中英文个人身份证件或护照(确定年满16周岁)
(2)2寸彩色证件照一张
四、报名注册ACCA条件,具备以下3条中的1条即可:
1、教育部认可的高等院校在校生(本科在校),顺利完成大一的课程考试,即可报名成为ACCA的正式学员;
2、凡具有教育部承认的大专以上学历,即可报名成为ACCA的正式学员;
3、未符合1、2项报名资格的申请者,可以先申请参加FIA(Foundations
in Accountancy)基础财务资格考试。在完成FAB(基础商业会计)、FMA(基础管理会计)、FFA(基础财务会计)3门课程后,可以豁免ACCAF1-F3三门课程的考试,直接进入ACCA技能课程的考试。
五、注意事项
1、在ACCA官方的报考要求中,大专以上学历在职人士,或本科以上顺利完成大一课程的在读大学生均可报考。为满足以上条件的,年满16周岁以上的还可通过FIA途径进行报考。不同的人群要按照不同的资料去准备。
2、ACCA具有系统性的考试体系,在报考条件上奉行宽进严出的准则,对于年满16周岁的中国公民来说,都可以报考。即使是从零基础开始,最终也有机会成为一个具备高端财务技能和职业操守的综合性人才,并胜任跨国集团的各类高级财务岗位。
希望本篇文章能够帮助到你们,如果还遇到其他不能解决的问题,要及时反馈给51题库考试学习网,我们会尽快帮您解决的哟!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) Discuss the key issues which will need to be addressed in determining the basic components of an
internationally agreed conceptual framework. (10 marks)
Appropriateness and quality of discussion. (2 marks)
(b) There are several issues which have to be addressed if an international conceptual framework is to be successfully developed.
These are:
(i) Objectives
Agreement will be required as to whether financial statements are to be produced for shareholders or a wide range of
users and whether decision usefulness is the key criteria or stewardship. Additionally there is the question of whether
the objective is to provide information in making credit and investment decisions.
(ii) Qualitative Characteristics
The qualities to be sought in making decisions about financial reporting need to be determined. The decision usefulness
of financial reports is determined by these characteristics. There are issues concerning the trade-offs between relevance
and reliability. An example of this concerns the use of fair values and historical costs. It has been argued that historical
costs are more reliable although not as relevant as fair values. Additionally there is a conflict between neutrality and the
traditions of prudence or conservatism. These characteristics are constrained by materiality and benefits that justify
costs.
(iii) Definitions of the elements of financial statements
The principles behind the definition of the elements need agreement. There are issues concerning whether ‘control’
should be included in the definition of an asset or become part of the recognition criteria. Also the definition of ‘control’
is an issue particularly with financial instruments. For example, does the holder of a call option ‘control’ the underlying
asset? Some of the IASB’s standards contravene its own conceptual framework. IFRS3 requires the capitalisation of
goodwill as an asset despite the fact that it can be argued that goodwill does not meet the definition of an asset in the
Framework. IAS12 requires the recognition of deferred tax liabilities that do not meet the liability definition. Similarly
equity and liabilities need to be capable of being clearly distinguished. Certain financial instruments could either be
liabilities or equity. For example obligations settled in shares.
(iv) Recognition and De-recognition
The principles of recognition and de-recognition of assets and liabilities need reviewing. Most frameworks have
recognition criteria, but there are issues over the timing of recognition. For example, should an asset be recognised when
a value can be placed on it or when a cost has been incurred? If an asset or liability does not meet recognition criteria
when acquired or incurred, what subsequent event causes the asset or liability to be recognised? Most frameworks do
not discuss de-recognition. (The IASB’s Framework does not discuss the issue.) It can be argued that an item should be
de-recognised when it does not meet the recognition criteria, but financial instruments standards (IAS39) require other
factors to occur before financial assets can be de-recognised. Different attributes should be considered such as legal
ownership, control, risks or rewards.
(v) Measurement
More detailed discussion of the use of measurement concepts, such as historical cost, fair value, current cost, etc are
required and also more guidance on measurement techniques. Measurement concepts should address initial
measurement and subsequent measurement in the form. of revaluations, impairment and depreciation which in turn
gives rise to issues about classification of gains or losses in income or in equity.
(vi) Reporting entity
Issues have arisen over what sorts of entities should issue financial statements, and which entities should be included
in consolidated financial statements. A question arises as to whether the legal entity or the economic unit should be the
reporting unit. Complex business arrangements raise issues over what entities should be consolidated and the basis
upon which entities are consolidated. For example, should the basis of consolidation be ‘control’ and what does ‘control’
mean?
(vii) Presentation and disclosure
Financial reporting should provide information that enables users to assess the amounts, timing and uncertainty of the
entity’s future cash flows, its assets, liabilities and equity. It should provide management explanations and the limitations
of the information in the reports. Discussions as to the boundaries of presentation and disclosure are required.
6 Certain practices have developed that threaten to damage the integrity and objectivity of professional accountants and
the reputation of the accounting profession.
Required:
Explain the following practices and associated ethical risks and discuss whether current ethical guidance is
sufficient:
(a) ‘lowballing’; (5 marks)
6 CERTAIN PRACTICES
Tutorial note: The answer which follows is indicative of the range of points which might be made. Other relevant material will
be given suitable credit.
(a) ‘Lowballing’
Explanation of term
‘Lowballing’ is the ‘loss-leading’ practice in which auditors compete for clients by reducing their fees for statutory audits.
Lower audit fees are then compensated by the auditor carrying out more lucrative non-audit work (e.g. consultancy and tax
advice). Audits may even be offered for free.
Such ‘predatory pricing’ may undercut an incumbent auditor to secure an appointment into which higher price consultancy
services may be sold.
Ethical risks
There is a risk of incompetence if the non-audit work does not materialise and the lowballing firm comes under pressure to
cut corners or resort to irregular practices (e.g. the falsification of audit working papers) in order to ‘keep within budget’.
However, a lack of audit quality may only be discovered if the situation arises that the company collapses and the auditors
are charged with negligence.
If, rather than comprise the quality of the audit, an audit firm substantially increases audit fees, a fee dispute could arise. In
this case the client might refuse to pay the higher fee. It could be difficult then for the firm to take the matter to arbitration
if the client was misled. Thus an advocacy threat may arise.
Financial dependence is a direct incentive that threatens independence. A self-interest threat therefore arises when, having
secured the audit, the audit firm needs the client to retain its services in order to recoup any losses initially incurred.
The provision of many other services gives rise to a self-review threat (as well as a self-interest threat).
Sufficiency of current ethical guidance
In current ethical guidance, the fact that an accountancy firm quotes a lower fee than other tendering firms is not improper,
providing that the prospective client is not misled about:
– the precise range of services that the quoted fee is intended to cover; and
– the likely level of fees for any other work undertaken.
This is clearly insufficient to prevent the practice of lowballing.
Legal prohibitions on the provision of many non-audit services (e.g. bookkeeping, financial information systems design and
implementation, valuation services, actuarial services, internal audit (outsourced), human resource services for executive
positions, investment and legal services) should make lowballing a riskier pricing strategy. This may curb the tendency to
lowball.
Lowballing could be eliminated if, for example, auditors were required to act ‘exclusively as auditors’. Although regulatory
environments have moved towards this there is not a total prohibition on non-audit services.
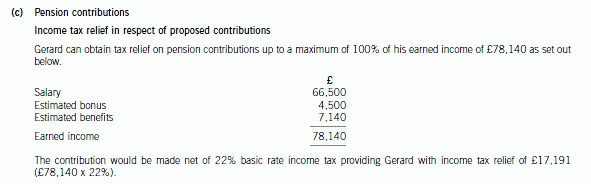
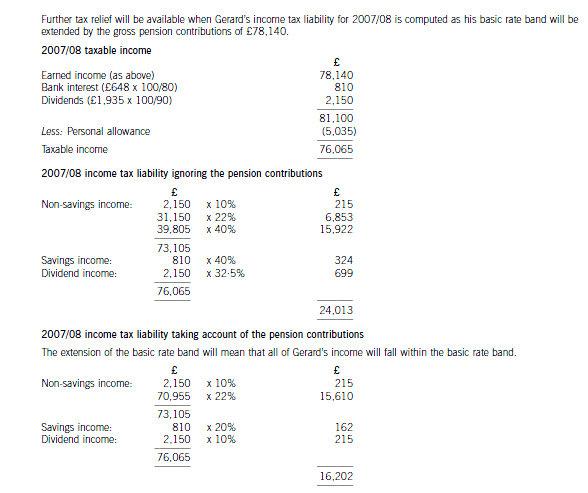
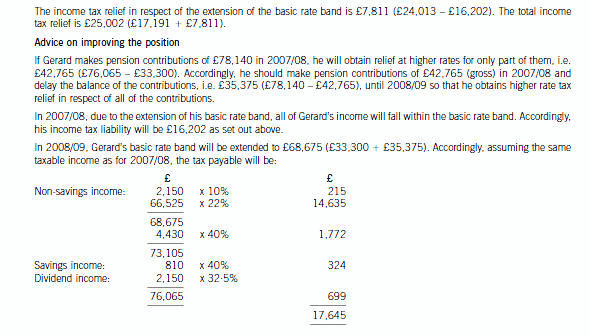
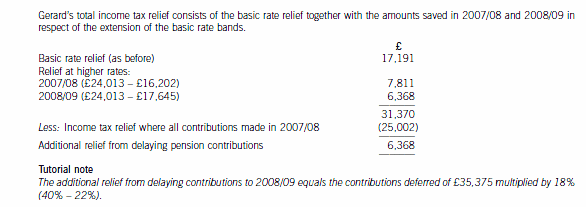
(c) Calculate and explain the amount of income tax relief that Gerard will obtain in respect of the pension
contributions he proposes to make in the tax year 2007/08 and contrast this with how his position could be
improved by delaying some of the contributions that he could have made in 2007/08 until 2008/09. You
should include relevant supporting calculations and quantify the additional tax savings arising as a result of
your advice.
You should ignore the proposed changes to the bonus scheme for this part of this question and assume that
Gerard’s income will not change in 2008/09. (12 marks)
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-03
- 2020-02-05
- 2020-02-15
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-30
- 2020-05-02
- 2020-05-17
- 2020-05-08
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-21
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-14
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-12-31
- 2020-04-12
- 2020-04-08
- 2020-05-10
- 2020-04-20
- 2020-02-19
- 2019-12-27
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-05
- 2020-05-17