3月考试取消,转而报考6月份考试的ACCA学员在这三个月该怎么复习?
发布时间:2020-03-08
由于2020年第一考试季(3月份)的ACCA考试已经取消,因此许多报考本次考试的考生都转而报名第二考试季(6月份)的考试。如何利用好多出来的三个月,是这些小伙伴关心的问题。鉴于此,51题库考试学习网在下面为大家带来ACCA考试备考方法的相关内容,以供参考。
首先,我们可以利用这一段时间进行查漏补缺。所谓查漏补缺,就是在ACCA考试中找到学习上的薄弱环节,及时采取有效措施进行补充完善,让我们可以全面化、系统化、有效化的吸收知识。在平常做完模拟试卷后,在试卷分析过程中,通过正确答案和错误答案的对比,要重点找到掌握不牢的知识点。接着,我们就应该去巩固这些知识点,不止是复习好课本和讲义上的基础知识,我们还要做好对知识的精细加工,做到举一反三。如此一来,我们可以更好的了解自己的不足,及时补救。
其次是不断对比成绩,找到自己的进步和不足。在这个阶段,我们要坚持练题。我们不但要多练,还要拿每次模考ACCA考试成绩与上次模考成绩对照,看是否比上次有进步。在对比时,考生不仅从分数上比,更要比到细处,细化到知识点。了解自己对不同知识点的熟悉程度。
也可以拿自己的成绩跟其他同学分数比。将其他学生分数作为参照,帮助自己找到相对处弱势的地方,及时补救。这样可以让知识点掌握更加牢固,对知识点的理解更深刻。
此外,我们在做练习题是也要注意反思。考试不仅仅是考查学生对知识的掌握情况,同时也是在检验学生学习方法的优劣和与应试能力的强弱。从考试情况来看,考生在考试中往往暴露粗心、做题方法不对、不会审题、检查不细等方面的不足,及时改正这些不足之处对后面的学习至关重要。同时,考生也要端正考试的态度,不能只关注分数,重要的是找到适合自己的高效学习法,培养适合自己的思考方式,提高自己的应试能力。要把ACCA报名条件和考试当成检验自己各方面能力的一次机遇。学会在考试中不断找准适合自己的学习方法。
以上就是关于ACCA考试学习方法的相关内容。51题库考试学习网提醒:这三个月的时间如果不利用好,可能会导致知识点因为时间推移出现记忆模糊的情况,因此小伙伴们不要松懈哦。最后,51题库考试学习网预祝准备参加2020年ACCA考试的小伙伴都能顺利通过。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) ‘Strategic positioning’ is about the way that a company as a whole is placed in its environment and concerns its
‘fit’ with the factors in its environment.
With reference to the case as appropriate, explain how a code of ethics can be used as part of a company’s
overall strategic positioning. (7 marks)
(b) Code of ethics and strategic positioning
Strategic positioning is about the way that a whole company is placed in its environment as opposed to the operational level,
which considers the individual parts of the organisation.
Ethical reputation and practice can be a key part of environmental ‘fit’, along with other strategic issues such as generic
strategy, quality and product range.
The ‘fit’ enables the company to more fully meet the expectations, needs and demands of its relevant stakeholders – in this
case, European customers.
The ‘quality’ of the strategic ‘fit’ is one of the major determinants of business performance and so is vital to the success of
the business.
HPC has carefully manoeuvred itself to have the strategic position of being the highest ethical performer locally and has won
orders on that basis.
It sees its strategic position as being the ethical ‘benchmark’ in its industry locally and protects this position against its parent
company seeking to impose a new code of ethics.
The ethical principles are highly internalised in Mr Hogg and in the company generally, which is essential for effective strategic
implementation.
5 GE Railways plc (GER) operates a passenger train service in Holtland. The directors have always focused solely on
the use of traditional financial measures in order to assess the performance of GER since it commenced operations
in 1992. The Managing Director of GER has asked you, as a management accountant, for assistance with regard to
the adoption of a balanced scorecard approach to performance measurement within GER.
Required:
(a) Prepare a memorandum explaining the potential benefits and limitations that may arise from the adoption of
a balanced scorecard approach to performance measurement within GER. (8 marks)
(a) To: Board of directors
From: Management Accountant
Date: 8 June 2007
The potential benefits of the adoption of a balanced scorecard approach to performance measurement within GER are as
follows:
A broader business perspective
Financial measures invariably have an inward-looking perspective. The balanced scorecard is wider in its scope and
application. It has an external focus and looks at comparisons with competitors in order to establish what constitutes best
practice and ensures that required changes are made in order to achieve it. The use of the balanced scorecard requires a
balance of both financial and non-financial measures and goals.
A greater strategic focus
The use of the balanced scorecard focuses to a much greater extent on the longer term. There is a far greater emphasis on
strategic considerations. It attempts to identify the needs and wants of customers and the new products and markets. Hence
it requires a balance between short term and long term performance measures.
A greater focus on qualitative aspects
The use of the balanced scorecard attempts to overcome the over-emphasis of traditional measures on the quantifiable aspects
of the internal operations of an organisation expressed in purely financial terms. Its use requires a balance between
quantitative and qualitative performance measures. For example, customer satisfaction is a qualitative performance measure
which is given prominence under the balanced scorecard approach.
A greater focus on longer term performance
The use of traditional financial measures is often dominated by financial accounting requirements, for example, the need to
show fixed assets at their historic cost. Also, they are primarily focused on short-term profitability and return on capital
employed in order to gain stakeholder approval of short term financial reports, the longer term or whole life cycle often being
ignored.
The limitations of a balanced scorecard approach to performance measurement may be viewed as follows:
The balanced scorecard attempts to identify the chain of cause and effect relationships which will provide the stimulus for
the future success of an organisation.
Advocates of a balanced scorecard approach to performance measurement suggest that it can constitute a vital component
of the strategic management process.
However, Robert Kaplan and David Norton, the authors of the balanced scorecard concept concede that it may not be suitable
for all firms. Norton suggests that it is most suitable for firms which have a long lead time between management action and
financial benefit and that it will be less suitable for firms with a short-term focus. However, other flaws can be detected in
the balanced scorecard.
The balanced scorecard promises to outline the theory of the firm by clearly linking the driver/outcome measures in a cause
and effect chain, but this will be difficult if not impossible to achieve.
The precise cause and effect relationships between measures for each of the perspectives on the balanced scorecard will be
complex because the driver and outcome measures for the various perspectives are interlinked. For example, customer
satisfaction may be seen to be a function of several drivers, such as employee satisfaction, manufacturing cycle time and
quality. However, employee satisfaction may in turn be partially driven by customer satisfaction and employee satisfaction
may partially drive manufacturing cycle time. A consequence of this non-linearity of the cause and effect chain (i.e., there is
non-linear relationship between an individual driver and a single outcome measure), is that there must be a question mark
as to the accuracy of any calculated correlations between driver and outcome measures. Allied to this point, any calculated
correlations will be historic. This implies that it will only be possible to determine the accuracy of cause and effect linkages
after the event, which could make the use of the balanced scorecard in dynamic industries questionable. If the market is
undergoing rapid evolution, for example, how meaningful are current measures of customer satisfaction or market share?
These criticisms do not necessarily undermine the usefulness of the balanced scorecard in presenting a more comprehensive
picture of organisational performance but they do raise doubts concerning claims that a balanced scorecard can be
constructed which will outline a clear cause and effect chain between driver and outcome measures and the firm’s financial
objectives.
(ii) authority; (3 marks)
(ii) AUTHORITY is the scope and amount of discretion given to a person to make decisions by virtue of the position held within the organisation. The authority and power structure of an organisation defines the part each member of the organisation is expected to perform. and the relationship between the organisation’s members so that its efforts are effective. The source of authority may be top down (as in formal organisations) or bottom up (as in social organizations and politics). In the scenario, authority is from the top and should be delegated downwards.
Moonstar Co is a property development company which is planning to undertake a $200 million commercial property development. Moonstar Co has had some difficulties over the last few years, with some developments not generating the expected returns and the company has at times struggled to pay its finance costs. As a result Moonstar Co’s credit rating has been lowered, affecting the terms it can obtain for bank finance. Although Moonstar Co is listed on its local stock exchange, 75% of the share capital is held by members of the family who founded the company. The family members who are shareholders do not wish to subscribe for a rights issue and are unwilling to dilute their control over the company by authorising a new issue of equity shares. Moonstar Co’s board is therefore considering other methods of financing the development, which the directors believe will generate higher returns than other recent investments, as the country where Moonstar Co is based appears to be emerging from recession.
Securitisation proposals
One of the non-executive directors of Moonstar Co has proposed that it should raise funds by means of a securitisation process, transferring the rights to the rental income from the commercial property development to a special purpose vehicle. Her proposals assume that the leases will generate an income of 11% per annum to Moonstar Co over a ten-year period. She proposes that Moonstar Co should use 90% of the value of the investment for a collateralised loan obligation which should be structured as follows:
– 60% of the collateral value to support a tranche of A-rated floating rate loan notes offering investors LIBOR plus 150 basis points
– 15% of the collateral value to support a tranche of B-rated fixed rate loan notes offering investors 12%
– 15% of the collateral value to support a tranche of C-rated fixed rate loan notes offering investors 13%
– 10% of the collateral value to support a tranche as subordinated certificates, with the return being the excess of receipts over payments from the securitisation process
The non-executive director believes that there will be sufficient demand for all tranches of the loan notes from investors. Investors will expect that the income stream from the development to be low risk, as they will expect the property market to improve with the recession coming to an end and enough potential lessees to be attracted by the new development.
The non-executive director predicts that there would be annual costs of $200,000 in administering the loan. She acknowledges that there would be interest rate risks associated with the proposal, and proposes a fixed for variable interest rate swap on the A-rated floating rate notes, exchanging LIBOR for 9·5%.
However the finance director believes that the prediction of the income from the development that the non-executive director has made is over-optimistic. He believes that it is most likely that the total value of the rental income will be 5% lower than the non-executive director has forecast. He believes that there is some risk that the returns could be so low as to jeopardise the income for the C-rated fixed rate loan note holders.
Islamic finance
Moonstar Co’s chief executive has wondered whether Sukuk finance would be a better way of funding the development than the securitisation.
Moonstar Co’s chairman has pointed out that a major bank in the country where Moonstar Co is located has begun to offer a range of Islamic financial products. The chairman has suggested that a Mudaraba contract would be the most appropriate method of providing the funds required for the investment.
Required:
(a) Calculate the amounts in $ which each of the tranches can expect to receive from the securitisation arrangement proposed by the non-executive director and discuss how the variability in rental income affects the returns from the securitisation. (11 marks)
(b) Discuss the benefits and risks for Moonstar Co associated with the securitisation arrangement that the non-executive director has proposed. (6 marks)
(c) (i) Discuss the suitability of Sukuk finance to fund the investment, including an assessment of its appeal to potential investors. (4 marks)
(ii) Discuss whether a Mudaraba contract would be an appropriate method of financing the investment and discuss why the bank may have concerns about providing finance by this method. (4 marks)
(a) An annual cash flow account compares the estimated cash flows receivable from the property against the liabilities within the securitisation process. The swap introduces leverage into the arrangement.
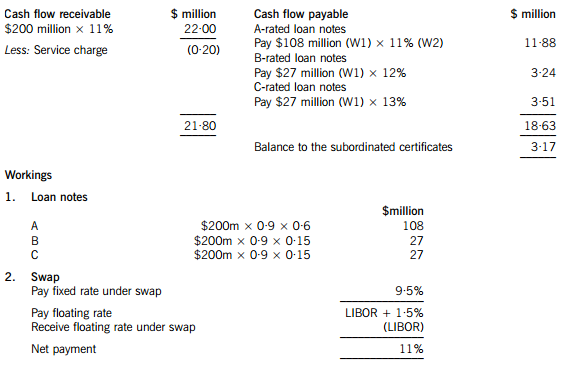
The holders of the certificates are expected to receive $3·17million on $18 million, giving them a return of 17·6%. If the cash flows are 5% lower than the non-executive director has predicted, annual revenue received will fall to $20·90 million, reducing the balance available for the subordinated certificates to $2·07 million, giving a return of 11·5% on the subordinated certificates, which is below the returns offered on the B and C-rated loan notes. The point at which the holders of the certificates will receive nothing and below which the holders of the C-rated loan notes will not receive their full income will be an annual income of $18·83 million (a return of 9·4%), which is 14·4% less than the income that the non-executive director has forecast.
(b) Benefits
The finance costs of the securitisation may be lower than the finance costs of ordinary loan capital. The cash flows from the commercial property development may be regarded as lower risk than Moonstar Co’s other revenue streams. This will impact upon the rates that Moonstar Co is able to offer borrowers.
The securitisation matches the assets of the future cash flows to the liabilities to loan note holders. The non-executive director is assuming a steady stream of lease income over the next 10 years, with the development probably being close to being fully occupied over that period.
The securitisation means that Moonstar Co is no longer concerned with the risk that the level of earnings from the properties will be insufficient to pay the finance costs. Risks have effectively been transferred to the loan note holders.
Risks
Not all of the tranches may appeal to investors. The risk-return relationship on the subordinated certificates does not look very appealing, with the return quite likely to be below what is received on the C-rated loan notes. Even the C-rated loan note holders may question the relationship between the risk and return if there is continued uncertainty in the property sector.
If Moonstar Co seeks funding from other sources for other developments, transferring out a lower risk income stream means that the residual risks associated with the rest of Moonstar Co’s portfolio will be higher. This may affect the availability and terms of other borrowing.
It appears that the size of the securitisation should be large enough for the costs to be bearable. However Moonstar Co may face unforeseen costs, possibly unexpected management or legal expenses.
(c) (i) Sukuk finance could be appropriate for the securitisation of the leasing portfolio. An asset-backed Sukuk would be the same kind of arrangement as the securitisation, where assets are transferred to a special purpose vehicle and the returns and repayments are directly financed by the income from the assets. The Sukuk holders would bear the risks and returns of the relationship.
The other type of Sukuk would be more like a sale and leaseback of the development. Here the Sukuk holders would be guaranteed a rental, so it would seem less appropriate for Moonstar Co if there is significant uncertainty about the returns from the development.
The main issue with the asset-backed Sukuk finance is whether it would be as appealing as certainly the A-tranche of the securitisation arrangement which the non-executive director has proposed. The safer income that the securitisation offers A-tranche investors may be more appealing to investors than a marginally better return from the Sukuk. There will also be costs involved in establishing and gaining approval for the Sukuk, although these costs may be less than for the securitisation arrangement described above.
(ii) A Mudaraba contract would involve the bank providing capital for Moonstar Co to invest in the development. Moonstar Co would manage the investment which the capital funded. Profits from the investment would be shared with the bank, but losses would be solely borne by the bank. A Mudaraba contract is essentially an equity partnership, so Moonstar Co might not face the threat to its credit rating which it would if it obtained ordinary loan finance for the development. A Mudaraba contract would also represent a diversification of sources of finance. It would not require the commitment to pay interest that loan finance would involve.
Moonstar Co would maintain control over the running of the project. A Mudaraba contract would offer a method of obtaining equity funding without the dilution of control which an issue of shares to external shareholders would bring. This is likely to make it appealing to Moonstar Co’s directors, given their desire to maintain a dominant influence over the business.
The bank would be concerned about the uncertainties regarding the rental income from the development. Although the lack of involvement by the bank might appeal to Moonstar Co's directors, the bank might not find it so attractive. The bank might be concerned about information asymmetry – that Moonstar Co’s management might be reluctant to supply the bank with the information it needs to judge how well its investment is performing.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-05-08
- 2020-02-11
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-29
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-28
- 2020-04-21
- 2020-04-19
- 2021-06-26
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-02-02
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-05
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-27
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-29
- 2020-05-01
- 2020-05-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-01
- 2020-05-14
- 2020-04-21