新疆考生想知道的ACCA国际会计师考试的几种题型
发布时间:2020-01-10
截止今日,关于2020年3月份ACCA考试的题型暂未公布,通常来说主要分为客观题、案例客观题、主观题三个部分,近些年一些相关的政策正在改革,所以一切要以ACCA官方发布的考试大纲为主。对于F阶段的机考,51题库考试学习网为大家做出了相应的解答:
ACCA 机考题型介绍
(一)客观题(Objective test questions/ OT questions)客观题是指这些单一的,题干较短的,并且自动判分的题目。每道客观题的分值为2分,考生必须回答的完全正确才可以得分,即使回答正确一部分,也不能得到分数。
(二)案例客观题 (OT case questions)
案例客观题是ACCA引入的新题型,每道案例客观题都是由一组与一个案例相关的客观题组成的,因此要求考生从多个角度来思考一个案例。这种题型能很好的反映出考生将如何在实践中完成这些任务。
(三) 主观题 (Constructed response questions/ CR
qustions)考生将使用电子表格程序和文字处理程序去完成主观题的回答。就像笔试中的主观题一样,答案最终将由专家判分。
ACCA考试各个科目的具体的考试题型介绍(以2016年9月的考试为例)
ACCA F1 (机考)考试科目 : 企业会计
时间 : 2 hours ;通过分数 : 50 ,F1 考试包含2个sections:
Section A
:46 道题目,其中30道题,每题2分;16道题,每题1分。总分值是76分。
Section B
:6道题目,每道题目4分。总分值24分。所有的题目都是必做题
ACCA F2 (机考)考试科目 : 管理会计
时间 : 2 hours 通过分数 : 50 ; F2 考试包含2个sections:
Section A
:25道题目,每道题目2分。总分值是70分。
Section B
:3道题目,每道题目10分。总分值是30分。
ACCA F3
(机考)考试科目 : 财务会计
时间 : 2 hours 通过分数 : 50,F3 考试包含2个sections
Section A
:25道题目,每道题目2分。总分值是70分。
Section B
:3道题目,每道题目10分。总分值是30分。
ACCA F4 (机考 & 纸考)考试科目 : 企业法和商法
时间 : 2 hours 通过分数 : 50 ,F4包含2个sections
Section A
:45道题目,其中25道题,每题2分;20道题,每题1分,总分值是70分。
Section B
:5道题目,每道题目6分。总分值30分。
ACCA F5 (机考 & 纸考)考试科目 : 绩效管理
时间 : 3 hours 通过分数 : 50,F5包含了3个sections
Section A
: 15道客观题,每题2分,总分30分。
Section B
: 3道案例题,每道案例题由5道客观题构成,每题2分,总分30分
Section C
: 2道案例分析题,每题20分,总分40分
ACCA F6 (机考 & 纸考)考试科目 : 税法 (UK版本)
时间 : 3 hours 通过分数 : 50,F6包含了3个sections:
Section A
:15道客观题,每题2分。Section A 总分30分。
Section B
:3道案例题,每道案例题由5道客观题构成,每题2分。Section B 总分30分
Section C
:3道案例分析题,每题10或 15分。Section C 总分40分
ACCA F7 (机考 & 纸考)考试科目 :财务报告
时间 :3 hours 通过分数 : 50 F7包含了3个sections
Section A
:15道客观题,每题2分。Section A 总分30分。
Section B
: 3道案例题,每道案例题由5道客观题构成,每题2分。Section B 总分30分
Section C
: 2道案例分析题,每题20分。Section C 总分40分。
ACCA F8 (机考 & 纸考)考试科目 :审计
时间 :3 hours 通过分数 : 50,F8包含了2个sections:
Section A:3道案例题,每道案例题由5道客观题构成,每题2分。Section A 总分30分
Section B:3道案例分析题,每道题目20或30分。Section B 总分 70分。
ACCA F9 (机考 & 纸考)考试科目 : 财务管理
时间 :3 hours 通过分数 : 50,F9包含了3个sections:
Section A
:15道客观题,每题2分。Section A 总分30分。
Section B
:3道案例题,每道案例题由5道客观题构成,每题2分。Section B 总分30分
Section C
:2道案例分析题,每题20分。Section C 总分40分。
P1 公司治理、P2 高级财务报告、P3 战略管理、P4 高级财务管理、P5 高级绩效管理
这几个paper,考试都分为2个section:
Section A
50分必做题;
Section B
3道25分的选做题,选2道,总分50分。
P6 高级税法、P7 高级审计 分为2个section:
Section A
2道必做题 总分60分。
Section B
3道选做题,选2道,总分40份。
看完以上的这些信息之后,相信大家对ACCA国际注册师也有了一定的了解,对此类考试感兴趣的小伙伴们可以持续关注51题库考试学习网哟~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
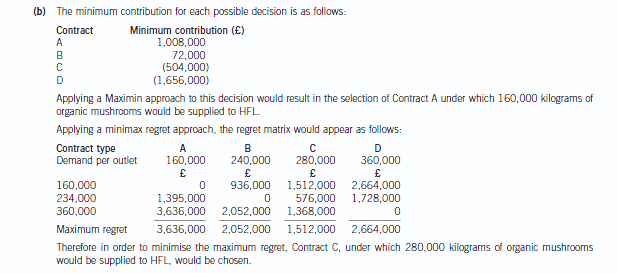
(b) Determine whether your decision in (a) would change if you were to use each of the Maximin and Minimax
regret decision criteria.
Your answer should be supported by relevant workings. (6 marks)
(b) Discuss the view that fair value is a more relevant measure to use in corporate reporting than historical cost.
(12 marks)
(b) The main disagreement over a shift to fair value measurement is the debate over relevance versus reliability. It is argued that
historical cost financial statements are not relevant because they do not provide information about current exchange values
for the entity’s assets which to some extent determine the value of the shares of the entity. However, the information provided
by fair values may be unreliable because it may not be based on arm’s-length transactions. Proponents of fair value
accounting argue that this measurement is more relevant to decision makers even if it is less reliable and would produce
balance sheets that are more representative of a company’s value. However it can be argued that relevant information that is
unreliable is of no use to an investor. One advantage of historical cost financial information is that it produces earnings
numbers that are not based on appraisals or other valuation techniques. Therefore, the income statement is less likely to be
subject to manipulation by management. In addition, historical cost balance sheet figures comprise actual purchase prices,
not estimates of current values that can be altered to improve various financial ratios. Because historical cost statements rely
less on estimates and more on ‘hard’ numbers, it can be said that historical cost financial statements are more reliable than
fair value financial statements. Furthermore, fair value measurements may be less reliable than historical costs measures
because fair value accounting provides management with the opportunity to manipulate the reported profit for the period.
Developing reliable methods of measuring fair value so that investors trust the information reported in financial statements is
critical.
Fair value measurement could be said to be more relevant than historical cost as it is based on market values and not entity
specific measurement on initial recognition, so long as fair values can be reliably measured. Generally the fair value of the
consideration given or received (effectively historical cost) also represents the fair value of the item at the date of initial
recognition. However there are many cases where significant differences between historical cost and fair value can arise on
initial recognition.
Historical cost does not purport to measure the value received. It cannot be assumed that the price paid can be recovered in
the market place. Hence the need for some additional measure of recoverable value and impairment testing of assets.
Historical cost can be an entity specific measurement. The recorded historical cost can be lower or higher than its fair value.
For example the valuation of inventory is determined by the costing method adopted by the entity and this can vary from
entity to entity. Historical cost often requires the allocation of costs to an asset or liability. These costs are attributed to assets,
liabilities and expenses, and are often allocated arbitrarily. An example of this is self constructed assets. Rules set out in
accounting standards help produce some consistency of historical cost measurements but such rules cannot improve
representational faithfulness.
Another problem with historical cost arises as regards costs incurred prior to an asset being recognised. Historical costs
recorded from development expenditure cannot be capitalised if they are incurred prior to the asset meeting the recognition
criteria in IAS38 ‘Intangible Assets’. Thus the historical cost amount does not represent the fair value of the consideration
given to create the asset.
The relevance of historical cost has traditionally been based on a cost/revenue matching principle. The objective has been to
expense the cost of the asset when the revenue to which the asset has contributed is recognised. If the historical cost of the
asset differs from its fair value on initial recognition then the matching process in future periods becomes arbitrary. The
measurement of assets at fair value will enhance the matching objective. Historical cost may have use in predicting future
net reported income but does not have any necessary implications for future cash flows. Fair value does embody the market’s
expectations for those future cash flows.
However, historical cost is grounded in actual transaction amounts and has existed for many years to the extent that it is
supported by practical experience and familiarity. Historical cost is accepted as a reliable measure especially where no other
relevant measurement basis can be applied.
(b) Comment on the need for ethical guidance for accountants on money laundering. (4 marks)
(b) Need for ethical guidance
■ Accountants (firms and individuals) working in a country that criminalises money laundering are required to comply with
anti-money laundering legislation and failure to do so can lead to severe penalties. Guidance is needed because:
– legal requirements are onerous;
– money laundering is widely defined; and
– accountants may otherwise be used, unwittingly, to launder criminal funds.
■ Accountants need ethical guidance on matters where there is conflict between legal responsibilities and professional
responsibilities. In particular, professional accountants are bound by a duty of confidentiality to their clients. Guidance
is needed to explain:
– how statutory provisions give protection against criminal action for members in respect of their confidentiality
requirements;
– when client confidentiality over-ride provisions are available.
■ Further guidance is needed to explain the interaction between accountants’ responsibilities to report money laundering
offences and other reporting responsibilities, for example:
– reporting to regulators;
– auditor’s reports on financial statements (ISA 700);
– reports to those charged with governance (ISA 260);
– reporting misconduct by members of the same body.
■ Professional accountants are required to communicate with each other when there is a change in professional
appointment (i.e. ‘professional etiquette’). Additional ethical guidance is needed on how to respond to a ‘clearance’ letter
where a report of suspicion has been made (or is being contemplated) in respect of the client in question.
Tutorial note: Although the term ‘professional clearance’ is widely used, remember that there is no ‘clearance’ that the
incumbent accountant can give or withhold.
■ Ethical guidance is needed to make accountants working in countries that do not criminalise money laundering aware
of how anti-money laundering legislation may nevertheless affect them. Such accountants may commit an offence if,
for example, they conduct limited assignments or have meetings in a country having anti-money laundering legislation
(e.g. UK, Ireland, Singapore, Australia and the United States).
(c) Assuming that she will survive until July 2009, advise on the lifetime inheritance tax (IHT) planning
measures that could be undertaken by Debbie, quantifying the savings that can be made. (7 marks)
For this question you should assume that the rates and allowances for 2004/05 apply throughout.
(c) Debbie survives until July 2009
Debbie should consider giving away some of her assets to her children, while ensuring that she still has enough to live on.
Such gifts would be categorised as PETs. Although Debbie will not survive seven years (at which point the gifts would fall out
of Debbie’s estate for IHT purposes), taper relief will reduce the amount chargeable to IHT. If gifts were made prior to July
2005, 40% taper relief would be available.
It is important to remember that Debbie’s annual exemptions will reduce the value of any PET when assets are gifted. Debbie
has not used her annual exemption for the last two years, and so she can gift £6,000 (2 x £3,000) in the current tax year
as well as £3,000 per year in future tax years. Debbie could therefore give away £18,000, saving tax of £7,200 (£18,000
x 40%). Debbie can also make small exempt gifts of up to £250 per donee per year.
Debbie should consider making gifts to Allison’s children instead of Allison (using, for example, an accumulation &
maintenance trust). This would ensure that the gifts were excluded from Allison’s estate.
It does not make sense for Debbie to gift shares in Dee Limited, as these qualify for full business property relief and therefore
are not subject to IHT.
As Andrew is shortly to be married, Debbie could give up to £5,000 in consideration of his marriage. This would save £2,000
in IHT.
Expenditure out of normal income is also exempt from IHT. This is where the transferor is left with sufficient income to
maintain his/her usual standard of living. Broadly, you need to demonstrate evidence of a prior commitment, or a settled
pattern of expenditure.
If substantial gifts are made, the donees would be advised to consider taking out insurance policies on Debbie’s life to cover
the potential tax liabilities that may arise on PETs in the event of her early death.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-03-05
- 2020-03-15
- 2020-04-09
- 2020-08-05
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-14
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-28
- 2020-01-29
- 2020-04-05
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-05-03
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-27
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-15
- 2021-08-05
- 2020-05-15
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-08