台湾考生想知道的ACCA国际会计师考试的几种题型
发布时间:2020-01-10
截止今日,关于2020年3月份ACCA考试的题型暂未公布,通常来说主要分为客观题、案例客观题、主观题三个部分,近些年一些相关的政策正在改革,所以一切要以ACCA官方发布的考试大纲为主。对于F阶段的机考,51题库考试学习网为大家做出了相应的解答:
ACCA 机考题型介绍
(一)客观题(Objective test questions/ OT questions)客观题是指这些单一的,题干较短的,并且自动判分的题目。每道客观题的分值为2分,考生必须回答的完全正确才可以得分,即使回答正确一部分,也不能得到分数。
(二)案例客观题 (OT case questions)
案例客观题是ACCA引入的新题型,每道案例客观题都是由一组与一个案例相关的客观题组成的,因此要求考生从多个角度来思考一个案例。这种题型能很好的反映出考生将如何在实践中完成这些任务。
(三) 主观题 (Constructed response questions/ CR
qustions)考生将使用电子表格程序和文字处理程序去完成主观题的回答。就像笔试中的主观题一样,答案最终将由专家判分。
ACCA考试各个科目的具体的考试题型介绍(以2016年9月的考试为例)
ACCA F1 (机考)考试科目 : 企业会计
时间 : 2 hours ;通过分数 : 50 ,F1 考试包含2个sections:
Section A
:46 道题目,其中30道题,每题2分;16道题,每题1分。总分值是76分。
Section B
:6道题目,每道题目4分。总分值24分。所有的题目都是必做题
ACCA F2 (机考)考试科目 : 管理会计
时间 : 2 hours 通过分数 : 50 ; F2 考试包含2个sections:
Section A
:25道题目,每道题目2分。总分值是70分。
Section B
:3道题目,每道题目10分。总分值是30分。
ACCA F3
(机考)考试科目 : 财务会计
时间 : 2 hours 通过分数 : 50,F3 考试包含2个sections
Section A
:25道题目,每道题目2分。总分值是70分。
Section B
:3道题目,每道题目10分。总分值是30分。
ACCA F4 (机考 & 纸考)考试科目 : 企业法和商法
时间 : 2 hours 通过分数 : 50 ,F4包含2个sections
Section A
:45道题目,其中25道题,每题2分;20道题,每题1分,总分值是70分。
Section B
:5道题目,每道题目6分。总分值30分。
ACCA F5 (机考 & 纸考)考试科目 : 绩效管理
时间 : 3 hours 通过分数 : 50,F5包含了3个sections
Section A
: 15道客观题,每题2分,总分30分。
Section B
: 3道案例题,每道案例题由5道客观题构成,每题2分,总分30分
Section C
: 2道案例分析题,每题20分,总分40分
ACCA F6 (机考 & 纸考)考试科目 : 税法 (UK版本)
时间 : 3 hours 通过分数 : 50,F6包含了3个sections:
Section A
:15道客观题,每题2分。Section A 总分30分。
Section B
:3道案例题,每道案例题由5道客观题构成,每题2分。Section B 总分30分
Section C
:3道案例分析题,每题10或 15分。Section C 总分40分
ACCA F7 (机考 & 纸考)考试科目 :财务报告
时间 :3 hours 通过分数 : 50 F7包含了3个sections
Section A
:15道客观题,每题2分。Section A 总分30分。
Section B
: 3道案例题,每道案例题由5道客观题构成,每题2分。Section B 总分30分
Section C
: 2道案例分析题,每题20分。Section C 总分40分。
ACCA F8 (机考 & 纸考)考试科目 :审计
时间 :3 hours 通过分数 : 50,F8包含了2个sections:
Section A:3道案例题,每道案例题由5道客观题构成,每题2分。Section A 总分30分
Section B:3道案例分析题,每道题目20或30分。Section B 总分 70分。
ACCA F9 (机考 & 纸考)考试科目 : 财务管理
时间 :3 hours 通过分数 : 50,F9包含了3个sections:
Section A
:15道客观题,每题2分。Section A 总分30分。
Section B
:3道案例题,每道案例题由5道客观题构成,每题2分。Section B 总分30分
Section C
:2道案例分析题,每题20分。Section C 总分40分。
P1 公司治理、P2 高级财务报告、P3 战略管理、P4 高级财务管理、P5 高级绩效管理
这几个paper,考试都分为2个section:
Section A
50分必做题;
Section B
3道25分的选做题,选2道,总分50分。
P6 高级税法、P7 高级审计 分为2个section:
Section A
2道必做题 总分60分。
Section B
3道选做题,选2道,总分40份。
看完以上的这些信息之后,相信大家对ACCA国际注册师也有了一定的了解,对此类考试感兴趣的小伙伴们可以持续关注51题库考试学习网哟~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
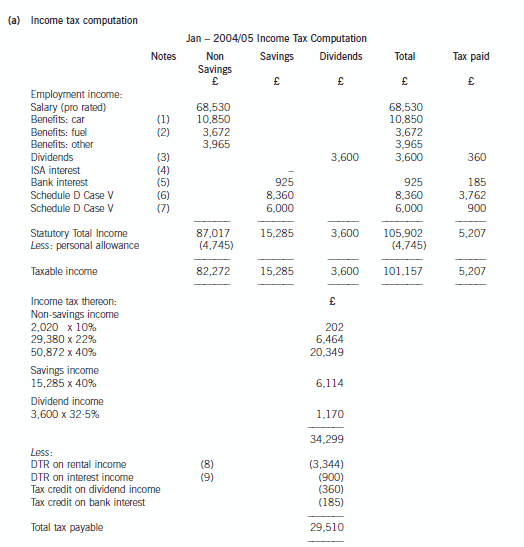
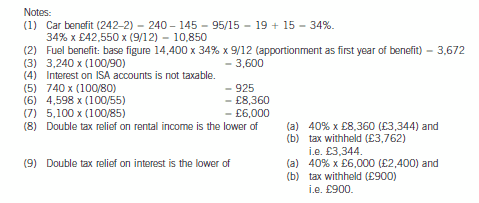
2 Assume that today’s date is 1 July 2005.
Jan is aged 45 and single. He is of Danish domicile but has been working in the United Kingdom since 1 May 2004
and intends to remain in the UK for the medium to long term. Although Jan worked briefly in the UK in 1986, he
has forgotten how UK taxation works and needs some assistance before preparing his UK income tax return.
Jan’s salary from 1 May 2004 was £74,760 per annum. Jan also has a company car – a Jaguar XJ8 with a list price
of £42,550 including extras, and CO2 emissions of 242g/km. The car was available to him from 1 July 2004. Free
petrol is provided by the company. Jan has other taxable benefits amounting to £3,965.
Jan’s other 2004/05 income comprises:
£
Dividend income from UK companies (cash received) 3,240
Interest received on an ISA account 230
Interest received on a UK bank account 740
Interest remitted from an offshore account (net of 15% withholding tax) 5,100
Income remitted from a villa in Portugal (net of 45% withholding tax) 4,598
The total interest arising on the offshore account was £9,000 (gross). In addition, Jan has not remitted other
Portuguese rental income arising in the year, totalling a further £1,500 (gross).
Jan informs you that his employer is thinking of providing him with rented accommodation while he looks for a house
to buy. The accommodation would be a two bedroom flat, valued at £155,000 with an annual value of £6,000. It
would be made available from 6 August 2005. The company will pay the rent of £600 per month for the first six
months. All other bills will be paid by Jan.
Jan also informs you that he has 25,000 ordinary shares in Gilet Ltd (‘Gilet’), an unquoted UK trading company. He
has held these shares since August 1986 when he bought 2,500 shares at £4.07 per share. In January 1994, a
bonus issue gave each shareholder nine shares for each ordinary share held. In the last week all Gilet’s shareholders
have received an offer from Jumper plc (‘Jumper’) who wishes to acquire the shares. Jumper has offered the following:
– 3 shares in Jumper (currently trading at £3.55 per share) for every 5 shares in Gilet, and
– 25p cash per share
Required:
(a) Calculate Jan’s 2004/05 income tax (IT) payable. (11 marks)
(iii) Identify and discuss an alternative strategy that may assist in improving the performance of CTC with
effect from 1 May 2009 (where only the products in (a) and (b) above are available for manufacture).
(4 marks)
(iii) If no new products are available then CTC must look to boost revenues obtained from its existing product portolio whilst
seeking to reduce product specific fixed overheads and the company’s other fixed overheads. In order to do this attention
should be focused on the marketing activities currently undertaken.
CTC should consider selling all of its products in ‘multi product’ packages as it might well be the case that the increased
contribution achieved from increased sales volumes would outweigh the diminution in contribution arising from
reductions in the selling price per unit of each product.
CTC could also apply target costing principles in order to reduce costs and thereby increase the margins on each of its
products. Value analysis should be undertaken in order to evaluate the value-added features of each product. For
example, the use of non-combustible materials in manufacture would be a valued added feature of such products
whereas the use of pins and metal fastenings which are potentially harmful to children would obviously not comprise
value added features. CTC should focus on delivering ‘value’ to the customer and in attempting to do so should seek to
identify all non-value activities in order that they may be eliminated and hence margins improved.
(c) You have been making preliminary inquiries regarding matters arising from the previous year’s audit of Di Rollo.
It has been revealed that no action has been taken in response to the management letter prepared by the previous
auditors. Di Rollo’s management has explained that this was because it was ‘poorly prepared’ and ‘unhelpful’.
Required:
Briefly describe various criteria against which the effectiveness of a management letter may be assessed.
(7 marks)
(c) Management letter effectiveness criteria
Tutorial note: Candidates at this level must know that a management letter is a letter of weakness (also called post-audit
letter). NO marks will be awarded for consideration of any other letters (e.g. management representation letters, engagement
letters).
■ Timeliness – a management letter should be issued as soon as possible after completion of the audit procedures giving
rise to comment. This is particularly important when audit work is carried out on more than one audit visit and where
it is a matter of urgency that management make improvements to their procedures (e.g. where there is evidence of
serious weakness).
■ Clarity – wording must be clear so that recipients understand the significance of weaknesses that are being drawn to
their attention. It is particularly important that implications are explained clearly in terms that will prompt management
to respond positively (e.g. drawing attention to the risks of financial loss arising).
■ Illustrative – specific illustrative examples (e.g. of where controls have not been evidenced) should aid management in
understanding the nature of the problem(s).
■ Constructive comments/advice – recommendations for improvements must be practicable (i.e. appropriate and costeffective
in the light of the client’s resources) if the client is to take corrective action.
■ Conciseness – unnecessary volume will distract management from new/additional matters that require their attention.
For example, matters adequately dealt with in the internal auditor’s report should not be repeated.
■ Factual accuracy is essential. Inaccuracies will not only aggravate the client and appear unprofessional but could, in rare
circumstances, result in liability. Similarly, the letter should not criticise (or ‘cast aspersions’) on individual staff members
if it is the system that is inadequate.
■ A suitable structure – for example ‘tiered’, where the report contains matters of varying levels of significance. By directing
different classes of matters to the appropriate level or area of responsibility action by management can be taken more
speedily and constructively.
Tutorial note: An alternative structure might be one that sequences those recommendations that improve
profitability/cash flows before those that deal with information systems.
■ Inclusion of staff responses – both to advise senior management of action proposed/being taken by their staff and to give
credit to recommendations for improvements where it is due (e.g. where client’s staff have proposed recommendations).
■ Inclusion of management’s response – an indication of the actions that management intends to take is more likely to
result in action being taken. Discussing findings with management first should also ensure their factual accuracy.
■ Client’s perspective – implications from the client’s viewpoint (e.g. in terms of cost savings) are more likely to be acted
on than those expressed from an audit perspective (e.g. in terms of lowered audit risk).
■ Professional tone – should not be offensive. Comments that fault management’s knowledge, competence, motives or
integrity are likely to provoke defensive reactions. Comments should be positive/constructive by emphasising
solutions/benefits.
Tutorial notes: Other points that candidates may include:
■ Inclusion of matters of future relevance
■ Cost effectiveness – minutes of discussions with management instead of a formal weakness letter
■ Not raising ‘people problems’ in such a formal communication (a confidential discussion is preferable).
(ii) Briefly discuss THREE disadvantages of using EVA? in the measurement of financial performance.
(3 marks)
(ii) Disadvantages of an EVA approach to the measurement of financial performance include:
(i) The calculation of EVA may be complicated due to the number of adjustments required.
(ii) It is difficult to use EVA for inter-firm and inter-divisional comparisons because it is not a ratio measure.
(iii) Economic depreciation is difficult to estimate and conflicts with generally accepted accounting principles.
Note: Other relevant discussion would be acceptable.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-04-20
- 2019-05-01
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-21
- 2020-03-28
- 2020-04-11
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-09-03
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-15
- 2019-08-03
- 2020-01-15
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-05-02
- 2020-02-20
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-01
- 2020-04-20
- 2020-05-23
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-05-02
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-03-14