重庆市考生们!2020年ACCA国际会计师考试科目、考试题题型题量!
发布时间:2020-01-09
2020年一月即将过去一半了,各位参加3月份ACCA考试的ACCAer们得要抓紧时间好好复习了呀~考试科目难度不了解?不知道怎么在有限的时间规划复习的侧重点?这些问题都通通不用担心,接下来51题库考试学习网就为大家讲解关于ACCA考试每个科目的难度,便于各位ACCAer们有重点的复习。
最简单的:知识课程原F1,F2,F3
这三个科目的内容在ACCA所有科目中属于最基础也是新手最容易入门的,难度不算太大,但仍然需要认真复习,且需要掌握的内容不多,都是会计学的基础。也正是因为这样,会计学本专业学生在完成第二年课程后可以免试这三科。这三科考试都为机考考试,且选择题居多,通过率按照往年的数据来看都在70%左右。
技能课程:原F4,F5,F6,F7,F9
这几门相对前三门难度有所提高,但相比较后面的专业阶段的考试科目来说,通过难度不算太大的。F4法律内容较多,需要背诵,但总体不难。F5是F2的进阶版,知识点重叠的部分很多。因此,只要F2学的好,通过F5也不在话下。F6关于税法,考试时以计算题为主,也正是因为计算题量大,对于中国考生来说,难度并不高,但这一部分对计算能力的考核的难度还是有的。F9和P1相似,以文字内容为主,想要通过考试需要动用记忆能力,记忆能力欠佳的考生建议反复多读和背,只要认真背过知识点的,总体难度一般。这几门中相对较难的是F7,从近几年的通过率来看是最低的,内容涉及到财务报表的编制,为P2专业阶段的考试打基础。想要编平报表,需要大量的练习历年真题是必不可少的。
AA(F8)和SBL(P1+P3),AAA(F7)
这三门之所以难度较高,原因在于大量的主观论述题。不少考生表示考到这几科才发现ACCA考试与其说是会计考试,不如说更像是英语作文考试。这几门难就难在需要站在一定高度去分析问题,且相比之前的F阶段考试需要更深层次的去了解。在F8阶段,需要了解具体的审计程序,而到了P7,则需要从事务所合伙人的角度来思考问题。考到这一等级,ACCA考试的核心才能体现出来,之前的F阶段的全部考试都是为此打基础。对于思维方式的养成初见成效,之前熟悉的备考应试方法显得捉襟见肘,考生唯有自己学会分析问题的方法,并用自己的语言阐述出来。
SBR(P2)和选修课程(P4-P7)
这几科之所以难,难在全为文字大题,光题目都有好几页。因此这不仅仅是对考生英语词汇量的挑战,不少同学表示光是读懂题目都已经非常有挑战性。但好在P4,P5,P6,P7四科是可以4选2报考的,考生可以根据自己对科目的掌握程度,结合自己的综合能力水平,选择自己最容易通过的科目报考。到这一阶段,考察的能力也是最多的,不仅需要记忆,理解相应的知识点,还需要用自己的语言表达观点。这就是对考生的记忆、理解、表达的这三方面的考核,但即便这样,经常也会有大神表示P5非常简单,其原因还是自己充分理解了考试内容和分析问题的方法。
F级跟P级的差别,就是F级只要花足够时间去学习,及格都不成问题,通过的话也是不在话下的。
但P级就有很多开放式答案,实在难说能掌握到什么程度。考试靠发挥、考心态、还有运气成分,因此建议大家在此阶段就需要更加努力的去复习和学习。
综合分析完所有ACCA考试科目,51题库考试学习网也收集到不少关于ACCAer自己的一些看法,看看他们眼中的考试科目难度是否和你想的一样呢?
首先,很多小伙伴说,在经历了前期4科的70+%通过率之后,F5忽然滑落到40%左右。这一点让不少新手ACCA都是十分胆怯的。对考取ACCA证书信心备受打击。
51题库考试学习网询认为,任何考试都有它的一些备考技巧,因此想要顺利通过F5只需要注意3个方面的问题即可。
以知识点为重,注意记忆
先看F5的考试题型:
Section A 15*2(选择题,共30分)
Section B 3*5*2(选择题,共30分)
Section C 2*20(我们俗称的“大题”,有计算和文字,共40分)
可以看出,光是选择题就占60分的比重,所以在F5的备考中,保证选择题不丢分是重中之重。因此建议大家可以多练习真题才可以,将章节的大框架理解到位。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) Explain the meaning of Stephanie’s comment: ‘I would like to get risk awareness embedded in the culture
at the Southland factory.’ (5 marks)
Embedded risk
Risk awareness is the knowledge of the nature, hazards and probabilities of risk in given situations. Whilst management will
typically be more aware than others in the organisation of many risks, it is important to embed awareness at all levels so as
to reduce the costs of risk to an organisation and its members (which might be measured in financial or non-financial terms).
In practical terms, embedding means introducing a taken-for-grantedness of risk awareness into the culture of an organisation
and its internal systems. Culture, defined in Handy’s terms as ‘the way we do things round here’ underpins all risk
management activity as it defines attitudes, actions and beliefs.
The embedding of risk awareness into culture and systems involves introducing risk controls into the process of work and the
environment in which it takes place. Risk awareness and risk mitigation become as much a part of a process as the process
itself so that people assume such measures to be non-negotiable components of their work experience. In such organisational
cultures, risk management is unquestioned, taken for granted, built into the corporate mission and culture and may be used
as part of the reward system.
Tutorial note: other meaningful definitions of culture in an organisational context are equally acceptable.
The following trial balance relates to Sandown at 30 September 2009:
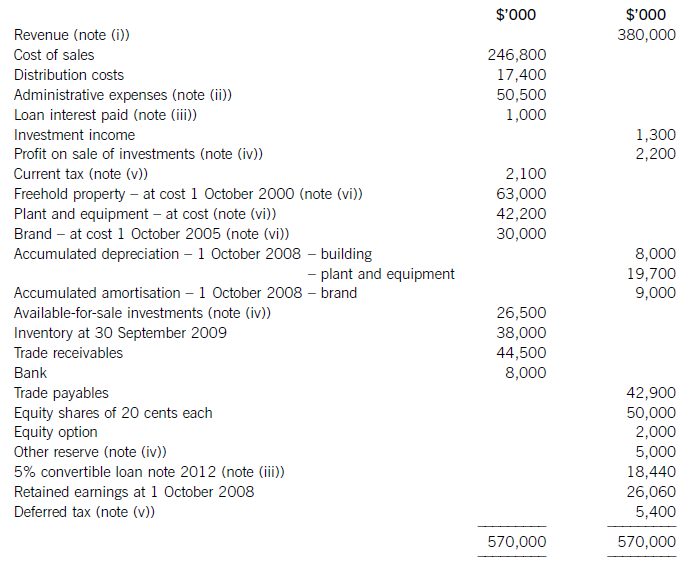
The following notes are relevant:
(i) Sandown’s revenue includes $16 million for goods sold to Pending on 1 October 2008. The terms of the sale are that Sandown will incur ongoing service and support costs of $1·2 million per annum for three years after the sale. Sandown normally makes a gross profit of 40% on such servicing and support work. Ignore the time value of money.
(ii) Administrative expenses include an equity dividend of 4·8 cents per share paid during the year.
(iii) The 5% convertible loan note was issued for proceeds of $20 million on 1 October 2007. It has an effective interest rate of 8% due to the value of its conversion option.
(iv) During the year Sandown sold an available-for-sale investment for $11 million. At the date of sale it had a
carrying amount of $8·8 million and had originally cost $7 million. Sandown has recorded the disposal of the
investment. The remaining available-for-sale investments (the $26·5 million in the trial balance) have a fair value of $29 million at 30 September 2009. The other reserve in the trial balance represents the net increase in the value of the available-for-sale investments as at 1 October 2008. Ignore deferred tax on these transactions.
(v) The balance on current tax represents the under/over provision of the tax liability for the year ended 30 September 2008. The directors have estimated the provision for income tax for the year ended 30 September 2009 at $16·2 million. At 30 September 2009 the carrying amounts of Sandown’s net assets were $13 million in excess of their tax base. The income tax rate of Sandown is 30%.
(vi) Non-current assets:
The freehold property has a land element of $13 million. The building element is being depreciated on a
straight-line basis.
Plant and equipment is depreciated at 40% per annum using the reducing balance method.
Sandown’s brand in the trial balance relates to a product line that received bad publicity during the year which led to falling sales revenues. An impairment review was conducted on 1 April 2009 which concluded that, based on estimated future sales, the brand had a value in use of $12 million and a remaining life of only three years.
However, on the same date as the impairment review, Sandown received an offer to purchase the brand for
$15 million. Prior to the impairment review, it was being depreciated using the straight-line method over a
10-year life.
No depreciation/amortisation has yet been charged on any non-current asset for the year ended 30 September
2009. Depreciation, amortisation and impairment charges are all charged to cost of sales.
Required:
(a) Prepare the statement of comprehensive income for Sandown for the year ended 30 September 2009.
(13 marks)
(b) Prepare the statement of financial position of Sandown as at 30 September 2009. (12 marks)
Notes to the financial statements are not required.
A statement of changes in equity is not required.
(i)IAS18Revenuerequiresthatwheresalesrevenueincludesanamountforaftersalesservicingandsupportcoststhenaproportionoftherevenueshouldbedeferred.Theamountdeferredshouldcoverthecostandareasonableprofit(inthiscaseagrossprofitof40%)ontheservices.Astheservicingandsupportisforthreeyearsandthedateofthesalewas1October2008,revenuerelatingtotwoyears’servicingandsupportprovisionmustbedeferred:($1·2millionx2/0·6)=$4million.Thisisshownas$2millioninbothcurrentandnon-currentliabilities.
(ii) State the principal audit procedures to be performed on the consolidation schedule of the Rosie Group.
(4 marks)
(ii) Audit procedures on the consolidation schedule of the Rosie Group:
– Agree correct extraction of individual company figures by reference to individual company audited financial
statements.
– Cast and cross cast all consolidation schedules.
– Recalculate all consolidation adjustments, including goodwill, elimination of pre acquisition reserves, cancellation
of intercompany balances, fair value adjustments and accounting policy adjustments.
– By reference to prior year audited consolidated accounts, agree accounting policies have been consistently applied.
– Agree brought down figures to prior year audited consolidated accounts and audit working papers (e.g. goodwill
figures for Timber Co and Ben Co, consolidated reserves).
– Agree that any post acquisition profits consolidated for Dylan Co arose since the date of acquisition by reference to
date of control passing per the purchase agreement.
– Reconcile opening and closing group reserves and agree reconciling items to group financial statements.
(ii) Can we entertain our clients as a gesture of goodwill or is corporate hospitality ruled out? (3 marks)
Required:
For EACH of the three FAQs, explain the threats to objectivity that may arise and the safeguards that should
be available to manage them to an acceptable level.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three questions.
(ii) Corporate hospitality
A partner in an audit firm is obviously in a position to influence the conduct and outcome of an audit. Therefore a
partner being on ‘too friendly’ terms with an audit client creates a familiarity threat. Other members of the audit team
may not exert as much influence on the audit.
A self-interest threat may also be perceived (e.g. if corporate hospitality is provided to keep a prestigious client).
There is no absolute prohibition against corporate hospitality provided:
■ the value attached to such hospitality is ‘insignificant’; and
■ the ‘frequency, nature and cost’ of the hospitality is reasonable.
Thus, flying the directors of an audit client for weekends away could be seen as significant. Similarly, entertaining an
audit client on a regular basis could be seen as unacceptable.
Partners and staff of Boleyn will need to be objective in their assessments of the significance or reasonableness of the
hospitality offered. (Would ‘a reasonable and informed third party’ conclude that the hospitality will or is likely to be
seen to impair your objectivity?)
If they have any doubts they should discuss the matter in the first instance with the audit engagement partner, who
should refer the matter to the ethics partner if in doubt.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-03-26
- 2020-03-27
- 2020-05-20
- 2019-01-04
- 2020-04-25
- 2020-04-16
- 2020-04-30
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-12-29
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-03-14
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-14
- 2020-04-19
- 2019-01-11
- 2020-04-25
- 2020-03-14
- 2020-02-14
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-23