消息!关于职场咖怎样平衡ACCA和工作呢?
发布时间:2020-05-21
大家知道 ACCA报名考试吗?那么关于职场咖怎样平衡ACCA和工作呢?带着这个问题,我们一起来了解下吧!
对于在职学习与在校学生情况会有些不同,在职考试需要平衡工作和学习时间,有时到家已经非常疲惫了,还要坐在学习桌上再学习几个小时。早已经不同于大学时,除了学习就是休息的生活了。
每个人情况不同,找到适合自己的学习方法最重要。固定时间进行学习每个人都是需要一定的压力的,如果不给自己固定学习时间进行学习的话,面对繁忙的工作,你的学习计划只能是一拖再拖。
由于下班时间不能固定,加班对于一些职场人士来说可能是家常便饭。既然晚上的学习时间不能够保证,那可以选择早上的时间进行学习。
早上是一天最清醒的时间,早起一个小时、两个小时也并不是十分困难的事情。且早上时间没有人打扰,工作也不会一大早就催你,这个时间进行学习往往会达到事半功倍的效果。
同时周末的时间也可以充分利用起来,大块的宝贵时间对于职场人来说真的难能可贵。可以拾遗补缺或者到了后期刷完整的卷子。
制定学习计划 完整的制定计划可能对于职场人士来说有些难,因为生活总是被工作填满,计划也赶不上变化快。
但是我们可以利用碎片化时间进行计划的制定,比如在地铁上、在电梯里、或者是想要拿出手机刷微博的时候,你完全可以在手机日历上制定一下近期的计划,有需要修正的时候及时修正,但你所制定的计划必须是可行的,否则会使自己没有信心,不想去完成。
这样一来,你就会对自己的学习进度有一个完整的把握,这对ACCA的学习时非常重要的。
ACCA总部推荐学员使用双币信用卡在线考试报名。这样将可以及时确认报名成功并且可以享受提前考试报名时段的优惠价格。
报名考试所需费用要一次交清吗?
不是的,要是一次缴清费用,那你就要荷包大出血了!估计连土都吃不起了,ACCA注册报名时只需交注册费,以后再逐项交纳免试费、年费、考试费。
考生可以随时关注自己的账单,并且注册后未及时上缴年费,会收到催缴邮件,补上就可以了。考试费用根据每次的报考科目和报考时间段来进行缴费。
以上就是关于考试的全部内容了,如果想要了解更多关于考试的信息,大家可以来关注51题库考试学习网哦,51题库考试学习网每天会为大家更新和考试相关的内容的。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(ii) On 1 July 2006 Petrie introduced a 10-year warranty on all sales of its entire range of stainless steel
cookware. Sales of stainless steel cookware for the year ended 31 March 2007 totalled $18·2 million. The
notes to the financial statements disclose the following:
‘Since 1 July 2006, the company’s stainless steel cookware is guaranteed to be free from defects in
materials and workmanship under normal household use within a 10-year guarantee period. No provision
has been recognised as the amount of the obligation cannot be measured with sufficient reliability.’
(4 marks)
Your auditor’s report on the financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2006 was unmodified.
Required:
Identify and comment on the implications of these two matters for your auditor’s report on the financial
statements of Petrie Co for the year ended 31 March 2007.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the matters above.
(ii) 10-year guarantee
$18·2 million stainless steel cookware sales amount to 43·1% of revenue and are therefore material. However, the
guarantee was only introduced three months into the year, say in respect of $13·6 million (3/4 × 18·2 million) i.e.
approximately 32% of revenue.
The draft note disclosure could indicate that Petrie’s management believes that Petrie has a legal obligation in respect
of the guarantee, that is not remote and likely to be material (otherwise no disclosure would have been required).
A best estimate of the obligation amounting to 5% profit before tax (or more) is likely to be considered material, i.e.
$90,000 (or more). Therefore, if it is probable that 0·66% of sales made under guarantee will be returned for refund,
this would require a warranty provision that would be material.
Tutorial note: The return of 2/3% of sales over a 10-year period may well be probable.
Clearly there is a present obligation as a result of a past obligating event for sales made during the nine months to
31 March 2007. Although the likelihood of outflow under the guarantee is likely to be insignificant (even remote) it is
probable that some outflow will be needed to settle the class of such obligations.
The note in the financial statements is disclosing this matter as a contingent liability. This term encompasses liabilities
that do not meet the recognition criteria (e.g. of reliable measurement in accordance with IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent
Liabilities and Contingent Assets).
However, it is extremely rare that no reliable estimate can be made (IAS 37) – the use of estimates being essential to
the preparation of financial statements. Petrie’s management must make a best estimate of the cost of refunds/repairs
under guarantee taking into account, for example:
■ the proportion of sales during the nine months to 31 March 2007 that have been returned under guarantee at the
balance sheet date (and in the post balance sheet event period);
■ the average age of cookware showing a defect;
■ the expected cost of a replacement item (as a refund of replacement is more likely than a repair, say).
If management do not make a provision for the best estimate of the obligation the audit opinion should be qualified
‘except for’ non-compliance with IAS 37 (no provision made). The disclosure made in the note to the financial
statements, however detailed, is not a substitute for making the provision.
Tutorial note: No marks will be awarded for suggesting that an emphasis of matter of paragraph would be appropriate
(drawing attention to the matter more fully explained in the note).
Management’s claim that the obligation cannot be measured with sufficient reliability does not give rise to a limitation
on scope on the audit. The auditor has sufficient evidence of the non-compliance with IAS 37 and disagrees with it.
(ii) Analyse the effect of delaying the sale of the business of the Stiletto Partnership to Razor Ltd until
30 April 2007 on Clint’s income tax and national insurance position.
You are not required to prepare detailed calculations of his income tax or national insurance liabilities.
(4 marks)
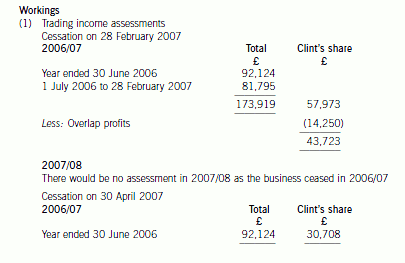
(ii) The implications of delaying the sale of the business
The implications of delaying the sale of the business until 30 April would have been as follows:
– Clint would have received an additional two months of profits amounting to £6,920 (£20,760 x 1/3).
– Clint’s trading income in 2006/07 would have been reduced by £13,015 (£43,723 – £30,708), much of which
would have been subject to income tax at 40%. His additional trading income in 2007/08 of £19,935 would all
have been taxed at 10% and 22%.
– Clint is entitled to the personal age allowance of £7,280 in both years. However, it is abated by £1 for every £2
by which his total income exceeds £20,100. Once Clint’s total income exceeds £24,590 (£20,100 + ((£7,280
– £5,035) x 2)), his personal allowance will be reduced to the standard amount of £5,035. Accordingly, the
increased personal allowance would not be available in 2006/07 regardless of the year in which the business was
sold. It is available in 2007/08 (although part of it is wasted) but would not have been if the sale of the business
had been delayed.
– Clint’s class 4 national insurance contributions in 2006/07 would have been reduced due to the fall in the level
of his trading income. However, much of the saving would be at 1% only. Clint is not liable to class 4 national
insurance contributions in 2007/08 as he is 65 at the start of the year.
– Changing the date on which the business was sold would have had no effect on Clint’s class 2 liability as he is
not required to make class 2 contributions once he is 65 years old.
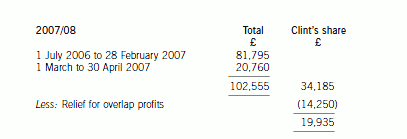
3 The Global Hotel Group (GHG) operates hotels in most of the developed countries throughout the world. The directors
of GHG are committed to a policy of achieving ‘growth’ in terms of geographical coverage and are now considering
building and operating another hotel in Tomorrowland. Tomorrowland is a developing country which is situated 3,000
kilometres from the country in which GHG’s nearest hotel is located.
The managing director of GHG recently attended a seminar on ‘the use of strategic and economic information in
planning organisational performance’.
He has called a board meeting to discuss the strategic and economic factors which should be considered before a
decision is made to build the hotel in Tomorrowland.
Required:
(a) Discuss the strategic and economic factors which should be considered before a decision is made to build
the hotel. (14 marks)
(a) Of vital importance is the need for reliable information on which to base the decision regarding the potential investment within
Tomorrowland, since the lack of such information will only serve to increase the risk profile of GHG.
The strategic factors that ought to be considered prior to a decision being made to build and operate a hotel in Tomorrowland
are as follows:
The competition
The key notion here is that of the position of GHG relative to its competitors who may have a presence or intend to have a
presence in Tomorrowland. The strategic management accounting system should be capable of coping with changes that can
and will inevitably occur in a dynamic business environment. Hence it is crucial that changes such as, the emergence of a
new competitor, are detected and reflected within strategic plans at the earliest opportunity.
The government
The attitude of the government of Tomorrowland towards foreign organisations requires careful consideration as inevitably the
government will be the country’s largest supplier, employer, customer and investor. The directors need to recognise that the
political environment of Tomorrowland could change dramatically with a change in the national government.
Planning and control of operations within Tomorrowland
Planning and control of operations within Tomorrowland will inevitably be more difficult as GHG might not possess sufficient
knowledge of the business environment within Tomorrowland. Indeed their nearest hotel is at least 3,000 kilometres away.
It is vital the GHG gain such knowledge prior to commencing operations within Tomorrowland in order to avoid undue risks.
The sociological–cultural constraints
While it is generally recognised that there is a growing acceptability of international brands this might not be the case with
regard to Tomorrowland. The attitude towards work, managers (especially foreign nationals) and capitalist organisations could
severely impact on the degree of success achieved within Tomorrowland. In this respect it is vital that consideration is given
to recognition of the relationships in economic life including demand, price, wages, training, and rates of labour turnover and
absenteeism.
Resource utilisation
A primary consideration relates to whether or not to use local labour in the construction of the hotel. The perceived
‘remoteness’ of Tomorrowland might make it an unattractive proposition for current employees of GHG, thereby presenting the
directors of GHG with a significant problem.
Communication
Consideration needs to be given to the communication problems that arise between different countries and in this respect
Tomorrowland is probably no exception. Language barriers will inevitably exist and this needs to be addressed at the earliest
opportunity to minimise any risks to GHG.
The economic factors that ought to be considered prior to a decision being made to build and operate a hotel in Tomorrowland
are as follows:
Resource availability
The hotel should be designed having given due consideration to the prevailing climatic conditions within Tomorrowland which
might necessitate the use of specific types of building materials. It might well be the case that such building materials are not
available locally, or are in such scarce supply in which case local supply would prove to be uneconomic.
Another consideration relates to local labour being available and reliable in terms of its quality.
Currency stability/restrictions
The stability of the currency within Tomorrowland assumes critical significance because profit repatriation is problematic in
situations where those profits are made in an unstable currency or one that is likely to depreciate against the home currency,
thereby precipitating sizeable losses on exchange. Any currency restrictions need to be given careful consideration. For
example, it might be the case that hotel guests would be prohibited from paying accommodation bills in a foreign currency
which would be problematic if the local currency was weak.
Legislation
All local and International legislation should be given careful consideration. It might be the case that local legislation via
various licences or legal requirements favour local hotels.
Demand
The potential demand within Tomorrowland will be linked to the local economy. It is a developing economy and this may
bode well for GHG. However, again the need for reliable information about the size of the market, the extent of competition,
likely future trends etc is of fundamental importance.
Financing
An important decision lies in the availability and associated costs of financing in Tomorrowland which might not have mature
enough capital markets due to its developmental state. Hence GHG might need to finance using alternative currencies.
Note: Other relevant comments would be acceptable.
(c) Explain the reasons for the concerns of the government of Happyland with companies such as TMC and
advise the directors of a strategy that might be considered in order to avoid being subject to any forthcoming
legislation concerning the environment. (5 marks)
(c) The government of Happyland will be concerned by the negative impact on the environment. The growth in the number of
children born in Happyland will have raised the demand for disposable nappies as is evidenced from the market size data
contained in the question. In some countries disposable nappies make up around 4% of all household waste and can take
up to five hundred years to decompose! The government will be concerned by the fact that trees are being destroyed in order
to keep babies and infant children in nappies. The disposal costs incurred by the government in terms of landfill etc will be
very high, hence its green paper on the effect of non-biodegradable products in Happyland. The costs of such operations as
the landfill for such products will need to be funded out of increased taxation.
It might be beneficial for the directors of TMC to develop more eco-friendly products such as washable nappies which, by
definition, are recyclable many times over during the life of the ‘product’. Many parents are now changing to ‘real nappies’
because they work out cheaper and better for the environment than disposables.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-02
- 2020-01-31
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-04-09
- 2020-05-08
- 2020-04-16
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-06-27
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-20
- 2020-01-01
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-03-14
- 2020-04-09
- 2020-03-14
- 2020-01-14
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-18