注意!ACCA考试需要通过几门呢?总有几门考试?
发布时间:2020-02-01
想知道ACCA需要通过几门考试吗?总有几门考试呢?赶紧来看看吧!
ACCA总共有15门,其中必须通过13门才能申请ACCA会员。
51题库考试学习网还给大家带来了ACCA考试主要注册流程:
1、准备注册所需材料。
(1)在校学生所需准备的注册材料:
中英文在校证明(原件必须为彩色扫描件),中英文成绩单(均需为加盖所在学校或学校教务部门公章的彩色扫描件),中英文个人身份证件或护照(原件必须为彩色扫描件、英文件必须为加盖所在学校或学校教务部门公章的彩色扫描件),2寸彩色护照用证件照一张,用于支付注册费用的国际双币信用卡或国际汇票。
(2)非在校学生所需准备的注册资料(符合学历要求):
中英文个人身份证件或护照(原件必须为彩色扫描件、英文件必须为加盖翻译公司翻译专用章的彩色扫描件),中英文学历证明(原件必须为彩色扫描件、英文件必须为加盖翻译公司翻译专用章的彩色扫描件,需提供中英文成绩单、国外学历均需提供成绩单),2寸彩色护照用证件照一张,用于支付注册费用的国际双币信用卡或国际汇票。
(3)非在校学生所需准备的注册资料(不符合学历要求-FIA形式):
中英文个人身份证件或护照(原件必须为彩色扫描件、英文件必须为加盖翻译公司翻译专用章或者学校教务部门公章的彩色扫描件),2寸彩色护照用证件照一张,用于支付注册费用的国际双币信用卡或国际汇票。
2、在全球官方网站进行注册:在线上传注册资料扫描文件,采用纸质材料将注册资料递交ACCA代表处。
3、支付注册费用。采用在线上传资料方式的必须在线支付。
4、查询注册进度:线上完成全部注册的约2周,纸质注册约6周。
好的,今天51题库考试学习网给大家分享的内容就是这些了,不知道小伙伴们是否清楚了呢?如果还有不了解的请继续关注51题库考试学习网。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) Describe the potential benefits for Hugh Co in choosing to have a financial statement audit. (4 marks)
(b) There are several benefits for Hugh Co in choosing a voluntary financial statement audit.
An annual audit will ensure that any material mistakes made by the part-qualified accountant in preparing the year end
financial statements will be detected. This is important as the directors will be using the year end accounts to review their
progress in the first year of trading and will need reliable figures to assess performance. An audit will give the directors comfort
that the financial statements are a sound basis for making business decisions.
Accurate first year figures will also enable more effective budgeting and forecasting, which will be crucial if rapid growth is to
be achieved.
The auditors are likely to use the quarterly management accounts as part of normal audit procedures. The auditors will be
able to advise Monty Parkes of any improvements that could be made to the management accounts, for example, increased
level of detail, more frequent reporting. Better quality management accounts will help the day-to-day running of the business
and enable a speedier response to any problems arising during the year.
As a by-product of the audit, a management letter (report to those charged with governance) will be produced, identifying
weaknesses and making recommendations on areas such as systems and controls which will improve the smooth running of
the business.
It is likely that Hugh Co will require more bank funding in order to expand, and it is likely that the bank would like to see
audited figures for review, before deciding on further finance. It will be easier and potentially cheaper to raise finance from
other providers with an audited set of financial statements.
As the business deals in cash sales, and retails small, luxury items there is a high risk of theft of assets. The external audit
can act as both a deterrent and a detective control, thus reducing the risk of fraud and resultant detrimental impact on the
financial statements.
Accurate financial statements will be the best basis for tax assessment and tax planning. An audit opinion will enhance the
credibility of the figures.
If the business grows rapidly, then it is likely that at some point in the future, the audit exemption limit will be exceeded and
thus an audit will become mandatory.
Choosing to have an audit from the first year of incorporation will reduce potential errors carried down to subsequent periods
and thus avoid qualifications of opening balances.
(ii) If a partner, who is an actuary, provides valuation services to an audit client, can we continue with the audit?
(3 marks)
Required:
For each of the three questions, explain the threats to objectivity that may arise and the safeguards that
should be available to manage them to an acceptable level.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three questions above.
(ii) Actuarial services to an audit client
IFAC’s ‘Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants’ does not deal specifically with actuarial valuation services but with
valuation services in general.
A valuation comprises:
■ making assumptions about the future;
■ applying certain methodologies and techniques;
■ computing a value (or range of values) for an asset, a liability or for a business as a whole.
A self-review threat may be created when a firm or network firm2 performs a valuation for a financial statement audit
client that is to be incorporated into the client’s financial statements.
As an actuarial valuation service is likely to involve the valuation of matters material to the financial statements (e.g. the
present value of obligations) and the valuation involves a significant degree of subjectivity (e.g. length of service), the
self-review threat created cannot be reduced to an acceptable level of the application of any safeguard. Accordingly:
■ such valuation services should not be provided; or
■ the firm should withdraw from the financial statement audit engagement.
If the net liability was not material to the financial statements the self-review threat may be reduced to an acceptable
level by the application of safeguards such as:
■ involving an additional professional accountant who was not a member of the audit team to review the work done
by the actuary;
■ confirming with the audit client their understanding of the underlying assumptions of the valuation and the
methodology to be used and obtaining approval for their use;
■ obtaining the audit client‘s acknowledgement of responsibility for the results of the work performed by the firm; and
■ making arrangements so that the partner providing the actuarial services does not participate in the audit
engagement.
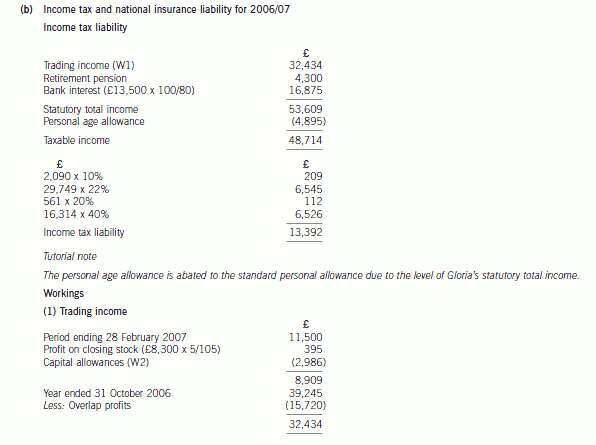
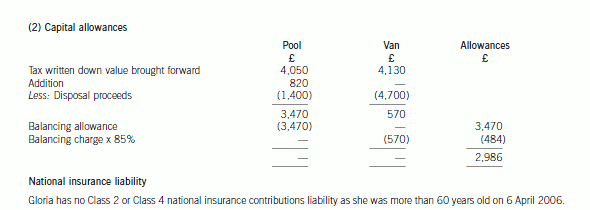
(b) Compute Gloria’s total income tax and national insurance liability for 2006/07. (7 marks)
(c) Critically discuss FOUR principal roles of non-executive directors and explain the potential tensions between
these roles that WM’s non-executive directors may experience in advising on the disclosure of the
overestimation of the mallerite reserve. (12 marks)
(c) Non-executive directors
Roles of NEDs
Non-executive directors have four principal roles.
The strategy role recognises that NEDs are full members of the board and thus have the right and responsibility to contribute
to the strategic success of the organisation for the benefit of shareholders. The enterprise must have a clear strategic direction
and NEDs should be able to bring considerable experience from their lives and business experience to bear on ensuring that
chosen strategies are sound. In this role they may challenge any aspect of strategy they see fit and offer advice or input to
help to develop successful strategy.
In the scrutinising or performance role, NEDs are required to hold executive colleagues to account for decisions taken and
company performance. In this respect they are required to represent the shareholders’ interests against the possibility that
agency issues arise to reduce shareholder value.
The risk role involves NEDs ensuring the company has an adequate system of internal controls and systems of risk
management in place. This is often informed by prescribed codes (such as Turnbull in the UK) but some industries, such as
chemicals, have other systems in place, some of which fall under ISO standards. In this role, NEDs should satisfy themselves
on the integrity of financial information and that financial controls and systems of risk management are robust and defensible.
Finally, the ‘people’ role involves NEDs overseeing a range of responsibilities with regard to the management of the executive
members of the board. This typically involves issues on appointments and remuneration, but might also involve contractual
or disciplinary issues and succession planning.
Tutorial note: these four roles are as described in the UK Higgs Report and are also contained in the Combined Code 2003.
Tensions in NED roles in the case
This refers to a potential tension in the loyalties of the NEDs. Although the NED is accountable, through the chairman to the
shareholders and thus must always act in the economic best interests of the shareholders, he or she is also a part of the board
of the company and they may, in some situations, advise discretion. Withholding information might be judged correct because
of strategic considerations or longer-term shareholder interests. In most situations, NEDs will argue for greater transparency,
less concealment and more clarity of how and why a given action will be in the interests of shareholders.
The case of mallerite overestimation places the WM NEDs in a position of some tension. Any instinct to conceal the full extent
of the overestimate of the reserve for the possible protection of the company’s short-term value must be balanced against the
duty to serve longer-term strategic interests and the public interest. Whilst concealment would protect the company’s
reputation and share price in the short term, it would be a duty of the NEDs to point out that WM should observe transparency
as far as possible in its dealing with the shareholders and other capital market participants.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-03-07
- 2019-08-02
- 2020-02-06
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-28
- 2020-04-21
- 2020-02-18
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-04-30
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-30
- 2020-01-29
- 2020-02-28
- 2020-03-26
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-29
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-12-31
- 2020-04-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-01