山东省考生想知道ACCA的科目F2怎么备考?
发布时间:2020-01-10
学习ACCA,不仅是为了给自己的简历上增添一个拿的出手的证书,更是因为ACCA完整的知识体系,充实自己的大学生活。我认为,每一份努力都会有回报,只要功夫下的多,就没有什么事情做不好。这一份ACCA MA(F2)的备考技巧请大家收藏起来哦~
报考建议
F2的考试一般建议大家在结课之后一个月左右考试,因为F2是一门刷题型的科目,需要留出足够的做题,并且考前也需要模拟考进行练习;但也不宜太晚考,有些需要记忆的知识点容易遗忘。因此,F2最简单也是最直截了当的复习技巧就是题海战术,当然大家可以根据自己的实际情况进行调整,如果备考时间充裕,也可以缩短备考时间,如果碰上了学校的考试周,或者有自己的比较忙的事情,也可以适当拉长。
备考建议
① 备考初期:F2主要以刷题为主。F2是管理会计,偏计算,但是计算水平要求其实也很低,重要的是细心点,把题看懂。
在ACCA的官网中也有样卷与模考卷可以练习,其中样卷是可以免费进入,进行练习的,模考卷的练习是需要付7英镑的费用。:
② 临考准备:如果大家已经看完网课,也做了一定量的习题了后,这个时候应该要明确自己薄弱的地方在哪里。哪部分知识点比较薄弱,就花费多一点的时间去复习,反之就少花费一点时间。建议大家可以像考试一样,在电脑上认真地花两个小时做一套模拟卷,并且进行批改,看看自己在考试中会遇到什么问题。
如果觉得两个小时的时间不够,做不完,说明做题的速度不够,需要提高做题速度。那么再做一遍题库,或者找其他的练习册再进行题海战略是必要的。
如果发现某个知识点的题目都需要花特别多的时间,或错误率非常高,那么说明对这部分的知识掌握的并不是很好,需要再次反复去巩固这部分的知识点,这部分有关的网课以及习题是需要再重新回顾1-2遍的。
如果觉得用电脑看题自己非常不适应,会非常影响自己的思路和速度,那么平时就不要在纸质的练习册上做题了,应该多练练,比如可以在电脑上做电子版的练习册或题库,使自己更适应机考。
总之大家可以通过模拟考的形式明确自己的弱点,进行加强后再在考试前练习一次,这样考试前就不会太紧张。但考试紧张也是会在所难的,所以就要要求大家及时调整心态,快速找回考试状态。
F2知识点总结
1. Data
and information:
Unprocessed
--->data; Processed --->information
2.
Quality of good information
“ACCURATE”
3.
Mission statement(abstract) ---> Objective(SMART) --->Strategy(Possible
course of action)
4.
Planning (establishing the objectives& selecting appropriate strategies)
5.
Control(compare plans with actual results, reviewed and made changes)
6. The
relationship between planning, decision making and control
7.
Management information Strategic information
幻想一步成功者突遭失败,会觉得浪费了时间,付出了精力,却认为没有任何收获;在失败面前,懦弱者痛苦迷茫,彷徨畏缩;而强者却坚持不懈,紧追不舍。各位ACCAer们加油,期待听到你们3月份考试成功的好消息~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) Describe the principal audit work to be performed in respect of the useful lives of Shire Oil Co’s rig platforms.
(6 marks)
(b) Principal audit work – useful life of rig platforms
Tutorial notes: The platforms are just one item of each rig. Candidates should not be awarded marks here for the matters
to be considered in the assessment of useful lives (since this is illustrated in the scenario). No marks will be awarded for
criticising management for estimating useful lives on a per platform. basis or for audit work on depreciation charges/carrying
amounts unrelated to the determination of useful lives.
■ Review of management’s annual assessment of the useful life of each rig at 31 December 2005 and corroboration of
any information that has led to a change in previous estimates. For example, for the abandoned rig, where useful life
has been assessed to be at an end, obtain:
? weather reports;
? incident report supported by photographs;
? insurance claim, etc.
■ Consider management’s past experience and expertise in estimating useful lives. For example, if all lives initially
assessed as short (c. 15 years) are subsequently lengthened (or long lives consistently shortened) this would suggest
that management is being over (under) prudent in its initial estimates.
■ Review of industry comparatives as published in the annual reports of other oil producers.
■ Comparison of actual maintenance costs against budgeted to confirm that the investment needed in maintenance, to
achieve expected life expectancy, is being made.
■ Comparison of actual output (oil extracted) against budgeted. If actual output is less than budgeted the economic life
of the platform. may be:
? shorter (e.g. because there is less oil to be extracted than originally surveyed); or
? longer (e.g. because the rate of extraction is less than budgeted).
Tutorial note: An increase in actual output can be explained conversely.
■ A review of the results of management’s impairment testing of each rig (i.e. the cash-generating unit of which each
platform. is a part).
■ Recalculations of cash flow projections (based on reasonable and supportable assumptions) discounted at a suitable
pre-tax rate.
Tutorial note: As the rigs will not have readily determinable net selling prices (each one being unique and not available
for sale) any impairment will be assessed by a comparison of value in use against carrying amount.
■ Review of working papers of geologist/quantity surveyor(s) employed by Shire supporting estimations of reserves used
in the determination of useful lives of rigs.
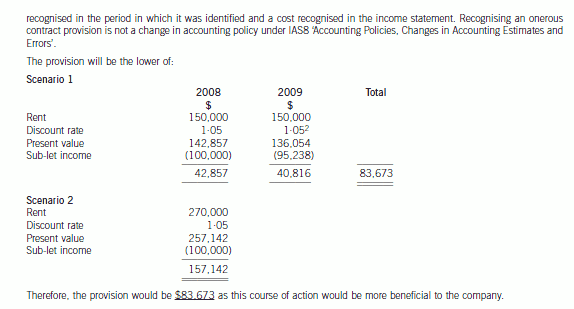
(d) Wader has decided to close one of its overseas branches. A board meeting was held on 30 April 2007 when a
detailed formal plan was presented to the board. The plan was formalised and accepted at that meeting. Letters
were sent out to customers, suppliers and workers on 15 May 2007 and meetings were held prior to the year
end to determine the issues involved in the closure. The plan is to be implemented in June 2007. The company
wish to provide $8 million for the restructuring but are unsure as to whether this is permissible. Additionally there
was an issue raised at one of the meetings. The operations of the branch are to be moved to another country
from June 2007 but the operating lease on the present buildings of the branch is non-cancellable and runs for
another two years, until 31 May 2009. The annual rent of the buildings is $150,000 payable in arrears on
31 May and the lessor has offered to take a single payment of $270,000 on 31 May 2008 to settle the
outstanding amount owing and terminate the lease on that date. Wader has additionally obtained permission to
sublet the building at a rental of $100,000 per year, payable in advance on 1 June. The company needs advice
on how to treat the above under IAS37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets’. (7 marks)
Required:
Discuss the accounting treatments of the above items in the financial statements for the year ended 31 May
2007.
Note: a discount rate of 5% should be used where necessary. Candidates should show suitable calculations where
necessary.
(d) A provision under IAS37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent assets’ can only be made in relation to the entity’s
restructuring plans where there is both a detailed formal plan in place and the plans have been announced to those affected.
The plan should identify areas of the business affected, the impact on employees and the likely cost of the restructuring and
the timescale for implementation. There should be a short timescale between communicating the plan and starting to
implement it. A provision should not be recognised until a plan is formalised.
A decision to restructure before the balance sheet date is not sufficient in itself for a provision to be recognised. A formal plan
should be announced prior to the balance sheet date. A constructive obligation should have arisen. It arises where there has
been a detailed formal plan and this has raised a valid expectation in the minds of those affected. The provision should only
include direct expenditure arising from the restructuring. Such amounts do not include costs associated with ongoing business
operations. Costs of retraining staff or relocating continuing staff or marketing or investment in new systems and distribution
networks, are excluded. It seems as though in this case a constructive obligation has arisen as there have been detailed formal
plans approved and communicated thus raising valid expectations. The provision can be allowed subject to the exclusion of
the costs outlined above.
Although executory contracts are outside IAS37, it is permissible to recognise a provision that is onerous. Onerous contracts
can result from restructuring plans or on a stand alone basis. A provision should be made for the best estimate of the excess
unavoidable costs under the onerous contract. This estimate should assess any likely level of future income from new sources.
Thus in this case, the rental income from sub-letting the building should be taken into account. The provision should be
(ii) The percentage change in revenue, total costs and net assets during the year ended 31 May 2008 that
would have been required in order to have achieved a target ROI of 20% by the Beetown centre. Your
answer should consider each of these three variables in isolation. State any assumptions that you make.
(6 marks)
(ii) The ROI of Beetown is currently 13·96%. In order to obtain an ROI of 20%, operating profit would need to increase to
(20% x $3,160,000) = $632,000, based on the current level of net assets. Three alternative ways in which a target
ROI of 20% could be achieved for the Beetown centre are as follows:
(1) Attempts could be made to increase revenue by attracting more clients while keeping invested capital and operating
profit per $ of revenue constant. Revenue would have to increase to $2,361,644, assuming that the current level
of profitability is maintained and fixed costs remain unchanged. The current rate of contribution to revenue is
$2,100,000 – $567,000 = $1,533,000/$2,100,000 = 73%. Operating profit needs to increase by $191,000
in order to achieve an ROI of 20%. Therefore, revenue needs to increase by $191,000/0·73 = $261,644 =
12·46%.
(2) Attempts could be made to decrease the level of operating costs by, for example, increasing the efficiency of
maintenance operations. This would have the effect of increasing operating profit per $ of revenue. This would
require that revenue and invested capital were kept constant. Total operating costs would need to fall by $191,000
in order to obtain an ROI of 20%. This represents a percentage decrease of 191,000/1,659,000 = 11·5%. If fixed
costs were truly fixed, then variable costs would need to fall to a level of $376,000, which represents a decrease
of 33·7%.
(3) Attempts could be made to decrease the net asset base of HFG by, for example, reducing debtor balances and/or
increasing creditor balances, while keeping turnover and operating profit per $ of revenue constant. Net assets
would need to fall to a level of ($441,000/0·2) = $2,205,000, which represents a percentage decrease
amounting to $3,160,000 – $2,205,000 = 955,000/3,160,000 = 30·2%.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-03-25
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-12
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-03-27
- 2020-05-02
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-06-25
- 2020-05-15
- 2020-04-24
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-04-25
- 2020-02-02
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-02
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-06
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-02-18
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-01-02
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-08-21
- 2020-04-14
- 2020-01-09