ACCA是什么?ACCA考了有用吗?
发布时间:2020-03-07
随着我国对外贸易的发展,ACCA也进入了越来越多人的视野当中。ACCA考试难度较高,且考试费用较多,许多小伙伴在心动之余,也不免想问花费这么多,ACCA究竟能带来哪些回报。鉴于此,51题库考试学习网在下面为大家带来有关2020年ACCA就业前景的相关信息,以供参考。
ACCA属于国际专业会计师组织,在国际上享有很高的声誉,与众多国际知名企业建立了密切的合作关系,比如跨国企业、各国地方企业、其他会计师组织、教育机构、以及联合国、世界银行等世界性组织。这些企业,都能为ACCA学员带来丰厚的薪资待遇以及较高的社会地位。
一般来说,ACCA学员毕业后的就职方向:外资银行金融投资分析师;跨国公司的财务、内审、金融、风险控制岗位;国际会计师事务所的审计师、咨询师岗位;国内境外上市公司的财务、金融分析岗位;国内审计师事务所的涉外部门主管等。这些都是非常诱人的岗位。
除了以上这些之外,ACCA会员的高含金量还体现在这些方面:
首先,ACCA会员资格在国际上得到广泛认可,尤其得到欧盟立法以及许多国家公司法的承认。因此可以说,拥有ACCA会员资格,就拥有了在世界各地就业的“通行证”。在任何地方,都能获得很好的工作。
其次,ACCA的课程就是根据现时商务社会对财会人员的实际要求进行开发、设计的,尤其是注意培养学员的分析能力和在复杂条件下的决策、判断能力。因此,ACCA课程所带来的系统的、高质量的培训会给予学生真才实学,让学员学成后能适应各种环境,并使会员成为具有全面管理素质的高级财务管理专家。具有胜任高薪工作的能力。
其次,ACCA会员在工商企业财务部门、(四大)审计/会计师事务所、金融机构和财政、税务部门从事财务以及财务管理工作,ACCA会员中有很多在世界各地大公司担任高级职位(财务经理、财务总监CFO,甚至总裁CEO)。所以,ACCA会员拥有很高的社会地位。
此外,ACCA还受到在中国的跨国公司、大型企业和国际“五大”会计公司全面认可。总的来说,ACCA学员年薪在中国50-100万RMB。
以上就是关于ACCA就业前景的相关情况。51题库考试学习网提醒:ACCA会员的良好待遇与其较高的考试难度是挂钩的,想要拥有这些令人心动的职位,还需要小伙伴们踏踏实实的去学习哦。最后,51题库考试学习网预祝准备参加2020年ACCA考试的小伙伴都能顺利通过。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(a) List and explain FOUR methods of selecting a sample of items to test from a population in accordance with ISA 530 (Redrafted) Audit Sampling and Other Means of Testing. (4 marks)
(b) List and explain FOUR assertions from ISA 500 Audit Evidence that relate to the recording of classes of
transactions. (4 marks)
(c) In terms of audit reports, explain the term ‘modified’. (2 marks)
(a)SamplingmethodsMethodsofsamplinginaccordancewithISA530AuditSamplingandOtherMeansofTesting:Randomselection.Ensureseachiteminapopulationhasanequalchanceofselection,forexamplebyusingrandomnumbertables.Systematicselection.Inwhichanumberofsamplingunitsinthepopulationisdividedbythesamplesizetogiveasamplinginterval.Haphazardselection.Theauditorselectsthesamplewithoutfollowingastructuredtechnique–theauditorwouldavoidanyconsciousbiasorpredictability.Sequenceorblock.Involvesselectingablock(s)ofcontinguousitemsfromwithinapopulation.Tutorialnote:Othermethodsofsamplingareasfollows:MonetaryUnitSampling.Thisselectionmethodensuresthateachindividual$1inthepopulationhasanequalchanceofbeingselected.Judgementalsampling.Selectingitemsbasedontheskillandjudgementoftheauditor.(b)Assertions–classesoftransactionsOccurrence.Thetransactionsandeventsthathavebeenrecordedhaveactuallyoccurredandpertaintotheentity.Completeness.Alltransactionsandeventsthatshouldhavebeenrecordedhavebeenrecorded.Accuracy.Theamountsandotherdatarelatingtorecordedtransactionsandeventshavebeenrecordedappropriately.Cut-off.Transactionsandeventshavebeenrecordedinthecorrectaccountingperiod.Classification.Transactionsandeventshavebeenrecordedintheproperaccounts.(c)AuditreporttermModified.Anauditormodifiesanauditreportinanysituationwhereitisinappropriatetoprovideanunmodifiedreport.Forexample,theauditormayprovideadditionalinformationinanemphasisofmatter(whichdoesnotaffecttheauditor’sopinion)orqualifytheauditreportforlimitationofscopeordisagreement.
(b) (i) Discusses the principles involved in accounting for claims made under the above warranty provision.
(6 marks)
(ii) Shows the accounting treatment for the above warranty provision under IAS37 ‘Provisions, Contingent
Liabilities and Contingent Assets’ for the year ended 31 October 2007. (3 marks)
Appropriateness of the format and presentation of the report and communication of advice. (2 marks)
(b) Provisions – IAS37
An entity must recognise a provision under IAS37 if, and only if:
(a) a present obligation (legal or constructive) has arisen as a result of a past event (the obligating event)
(b) it is probable (‘more likely than not’), that an outflow of resources embodying economic benefits will be required to settle
the obligation
(c) the amount can be estimated reliably
An obligating event is an event that creates a legal or constructive obligation and, therefore, results in an enterprise having
no realistic alternative but to settle the obligation. A constructive obligation arises if past practice creates a valid expectation
on the part of a third party. If it is more likely than not that no present obligation exists, the enterprise should disclose a
contingent liability, unless the possibility of an outflow of resources is remote.
The amount recognised as a provision should be the best estimate of the expenditure required to settle the present obligation
at the balance sheet date, that is, the amount that an enterprise would rationally pay to settle the obligation at the balance
sheet date or to transfer it to a third party. This means provisions for large populations of events such as warranties, are
measured at a probability weighted expected value. In reaching its best estimate, the entity should take into account the risks
and uncertainties that surround the underlying events.
Expected cash outflows should be discounted to their present values, where the effect of the time value of money is material
using a risk adjusted rate (it should not reflect risks for which future cash flows have been adjusted). If some or all of the
expenditure required to settle a provision is expected to be reimbursed by another party, the reimbursement should be
recognised as a separate asset when, and only when, it is virtually certain that reimbursement will be received if the entity
settles the obligation. The amount recognised should not exceed the amount of the provision. In measuring a provision future
events should be considered. The provision for the warranty claim will be determined by using the expected value method.
The past event which causes the obligation is the initial sale of the product with the warranty given at that time. It would be
appropriate for the company to make a provision for the Year 1 warranty of $280,000 and Year 2 warranty of $350,000,
which represents the best estimate of the obligation (see Appendix 2). Only if the insurance company have validated the
counter claim will Macaljoy be able to recognise the asset and income. Recovery has to be virtually certain. If it is virtually
certain, then Macaljoy may be able to recognise the asset. Generally contingent assets are never recognised, but disclosed
where an inflow of economic benefits is probable.
The company could discount the provision if it was considered that the time value of money was material. The majority of
provisions will reverse in the short term (within two years) and, therefore, the effects of discounting are likely to be immaterial.
In this case, using the risk adjusted rate (IAS37), the provision would be reduced to $269,000 in Year 1 and $323,000 in
Year 2. The company will have to determine whether this is material.
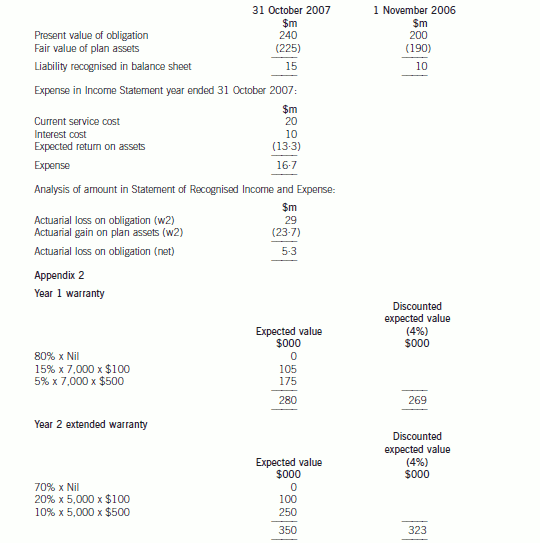
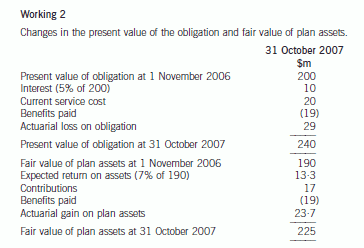
Appendix 1
The accounting for the defined benefit plan is as follows:

(b) Explain the matters you should consider before accepting an engagement to conduct a due diligence review
of MCM. (10 marks)
(b) Matters to be considered (before accepting the engagement)
Tutorial note: Although candidates may approach this part from a rote-learned list of ‘matters to consider’ it is important
that answer points be tailored, in so far as the information given in the scenario permits, to the specifics of Plaza and MCM.
It is critical that answer points should not contradict the scenario (e.g. assuming that it is Plaza’s auditor who has been
asked to undertake the assignment).
■ Information about Duncan Seymour – What is the relationship of the chief finance officer to Plaza (e.g. is he on the
management board)? By what authority is he approaching Andando to undertake this assignment?
■ The purpose of the assignment must be clarified. Duncan’s approach to Andando is ‘to advise on a bid’. However,
Andando cannot make executive decisions for a client but only provide the facts of material interest. Plaza’s
management must decide whether or not to bid and, if so, how much to bid.
■ The scope of the due diligence review. It seems likely that Plaza will be interested in acquiring all of MCM’s business
as its areas of operation coincide with Plaza’s. However it must be confirmed that Plaza is not merely interested in
acquiring only the National or International business of MCM.
■ Andando’s competence and experience – Andando should not accept the engagement unless the firm has experience in
undertaking due diligence assignments. Even then, the firm must have sufficient knowledge of the territories in which
the businesses operate to evaluate whether all facts of material interest to Plaza have been identified.
Tutorial note: Candidates should be querying their competence and experience in the fields of retailing and training
as though they were dealing with highly regulated or specialist industries such as banking or insurance.
■ Whether Andando has sufficient resources (e.g. representative/associated offices), if any, in Europe and Asia to
investigate MCM’s International business.
■ Any factors which might impair Andando’s objectivity in reporting to Plaza the facts uncovered by the due diligence
review. For example, if Duncan is closely connected with a partner in Andando or if Andando is the auditor of Frontiers.
Tutorial note: Candidates will not be awarded marks for going into ‘autopilot’ on independence issues. For example,
this is a one-off assignment so size of fee is not relevant. Andando holding shares in MCM is not possible (since whollyowned).
■ Plaza’s rationale for wishing to acquire MCM. Presumably it is significant that MCM operates in the same territories as
Plaza. Plaza may be wanting to provide extensive training programs in management, communications and marketing
to its workforce.
■ The relationship, if any, between Plaza and MCM in any of the territories. Plaza may be a major client of MCM. That
is, Plaza is currently out-sourcing training to MCM. Acquiring MCM would bring training in-house.
Tutorial note: Ascertaining what a purchaser hopes to gain from an acquisition before the assignment is accepted is
important. The facts to be uncovered for a merger from which synergy is expected will be different from those relevant
to acquiring an investment opportunity.
■ Time available – Andando must have sufficient time to find all facts that would be of material interest to Plaza before
disclosing their findings.
■ The acceptability of any limitations – whether there will be restrictions on Andando’s access to information held by MCM
(e.g. if there will not be access to board minutes) and personnel.
■ The degree of secrecy required – this may go beyond the normal duties of confidentiality not to disclose information to
outsiders (e.g. if unannounced staff redundancies could arise).
■ Why Plaza’s current auditors have not been asked to conduct the due diligence review – especially as they are
responsible for (and therefore capable of undertaking) the group audit covering the relevant countries.
■ Andando should be allowed to communicate with Plaza’s current auditor:
– to inform. them of the nature of the work they have been asked to undertake; and
– to enquire if there is any reason why they should not accept this assignment.
■ In taking on Plaza as a new client Andando may have a later opportunity to offer external audit and other services to
Plaza (e.g. internal audit).
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2021-06-26
- 2020-03-11
- 2019-01-04
- 2021-05-02
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-07
- 2020-04-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-03-06
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-04
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-30
- 2021-02-14
- 2020-04-11
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-19
- 2020-03-11
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-18