ACCA考试F3考试试题每日一练(2020-08-14)
发布时间:2020-08-14
为了帮助备考ACCA考试的小伙伴更好的备考,下面51题库考试学习网就分享给大家一些ACCA考试F3考试试题,感兴趣的小伙伴赶紧来练习吧。
1. Which of the
following are books of prime entry?
1 Sales day book
2 Cash book
3 Journal
4 Purchase ledger
A 1 and 2 only
B 1,2and3only
C 1 only
D All of them
答案:B
2. In which book
of prime entry will a business record debit notes in respect of goods which
have been sent back to suppliers?
A The sales returns day book
B The cash book
C The purchase returns day book
D The purchase day book
答案:C
3. Which one of
the following is not a qualitative characteristic of financial information
according to the Conceptual framework for Financial Reporting?
A Faithful representation
B Relevance
C Timeliness
D Accruals
答案:D
4. According to
the IASB Conceptual framework which of the following is not an objective of
financial statements?
A Providing information regarding the
financial position of a business
B Providing information regarding the
performance of a business
C Enabling users to assess the performance
of management to aid decision making
D Providing reliable investment advice
答案:D
5. Which of the
following statements about accounting concepts and policies is/are correct?
1 Companies should never change the
presentation or classification of items in their financial statements, even if
there is a significant change in the nature of operations.
2 Companies should create provisions in
times of company growth to be utilised in more difficult times, to smooth
profits.
A 1 only
B 2 only
C 1and2
D Both are incorrect
答案:D
以上是本次51题库考试学习网分享给大家的ACCA考试试题,备考的小伙伴抓紧时间练习一下吧。欲了解更多关于ACCA考试的试题,敬请关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
3 (a) Leigh, a public limited company, purchased the whole of the share capital of Hash, a limited company, on 1 June
2006. The whole of the share capital of Hash was formerly owned by the five directors of Hash and under the
terms of the purchase agreement, the five directors were to receive a total of three million ordinary shares of $1
of Leigh on 1 June 2006 (market value $6 million) and a further 5,000 shares per director on 31 May 2007,
if they were still employed by Leigh on that date. All of the directors were still employed by Leigh at 31 May
2007.
Leigh granted and issued fully paid shares to its own employees on 31 May 2007. Normally share options issued
to employees would vest over a three year period, but these shares were given as a bonus because of the
company’s exceptional performance over the period. The shares in Leigh had a market value of $3 million
(one million ordinary shares of $1 at $3 per share) on 31 May 2007 and an average fair value of
$2·5 million (one million ordinary shares of $1 at $2·50 per share) for the year ended 31 May 2007. It is
expected that Leigh’s share price will rise to $6 per share over the next three years. (10 marks)
Required:
Discuss with suitable computations how the above share based transactions should be accounted for in the
financial statements of Leigh for the year ended 31 May 2007.
(a) The shares issued to the management of Hash by Leigh (three million ordinary shares of $1) for the purchase of the company
would not be accounted for under IFRS2 ‘Share-based payment’ but would be dealt with under IFRS3 ‘Business
Combinations’.
The cost of the business combination will be the total of the fair values of the consideration given by the acquirer plus any
attributable cost. In this case the shares of Leigh will be fair valued at $6 million with $3 million being shown as share capital
and $3million as share premium. However, the shares issued as contingent consideration may be accounted for under IFRS2.
The terms of the issuance of shares will need to be examined. Where part of the consideration may be reliant on uncertain
future events, and it is probable that the additional consideration is payable and can be measured reliably, then it is included
in the cost of the business consideration at the acquisition date. However, the question to be answered in the case of the
additional 5,000 shares per director is whether the shares are compensation or part of the purchase price. There is a need
to understand why the acquisition agreement includes a provision for a contingent payment. It is possible that the price paid
initially by Leigh was quite low and, therefore, this then represents a further purchase consideration. However, in this instance
the additional payment is linked to continuing employment and, therefore, it would be argued that because of the link between
the contingent consideration and continuing employment that it represents a compensation arrangement which should be
included within the scope of IFRS2.
Thus as there is a performance condition, (the performance condition will apply as it is not a market condition) the substance
of the agreement is that the shares are compensation, then they will be fair valued at the grant date and not when the shares
vest. Therefore, the share price of $2 per share will be used to give compensation of $50,000 (5 x 5,000 x $2). (Under
IFRS3, fair value is measured at the date the consideration is provided and discounted to presented value. No guidance is
provided on what the appropriate discount rate might be. Thus the fair value used would have been $3 per share at 31 May
2007.) The compensation will be charged to the income statement and included in equity.
The shares issued to the employees of Leigh will be accounted for under IFRS2. The issuance of fully paid shares will be
presumed to relate to past service. The normal vesting period for share options is irrelevant, as is the average fair value of the
shares during the period. The shares would be expensed at a value of $3 million with a corresponding increase in equity.
Goods or services acquired in a share based payment transaction should be recognised when they are received. In the case
of goods then this will be when this occurs. However, it is somewhat more difficult sometimes to determine when services
are received. In a case of goods the vesting date is not really relevant, however, it is highly relevant for employee services. If
shares are issued that vest immediately then there is a presumption that these are a consideration for past employee services.
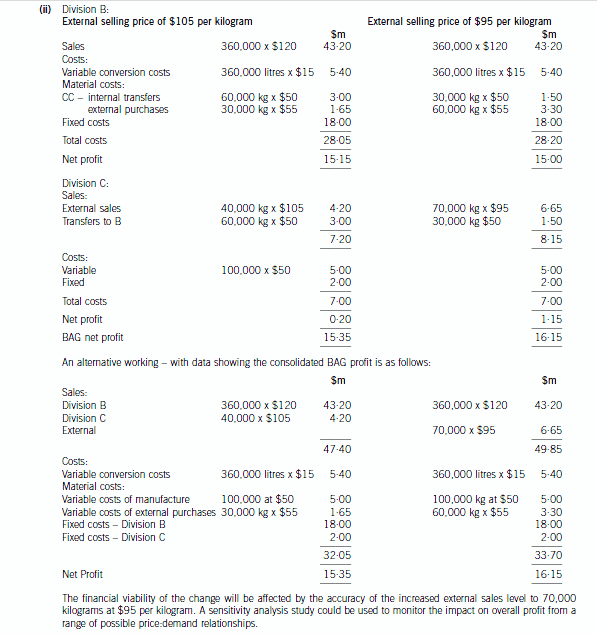
(ii) Division C is considering a decision to lower its selling price to customers external to the group to $95
per kilogram. If implemented, this decision is expected to increase sales to external customers to
70,000 kilograms.
Required:
For BOTH the current selling price of CC of $105 per kilogram and the proposed selling price of $95
per kilogram, prepare a detailed analysis of revenue, costs and net profits of BAG.
Note: in addition, comment on other considerations that should be taken into account before this selling
price change is implemented. (6 marks)
(b) Distinguish between strategic and operational risks, and explain why the secrecy option would be a source
of strategic risk. (10 marks)
(b) Strategic and operational risks
Strategic risks
These arise from the overall strategic positioning of the company in its environment. Some strategic positions give rise to
greater risk exposures than others. Because strategic issues typically affect the whole of an organisation and not just one or
more of its parts, strategic risks can potentially concern very high stakes – they can have very high hazards and high returns.
Because of this, they are managed at board level in an organisation and form. a key part of strategic management.
Operational risks
Operational risks refer to potential losses arising from the normal business operations. Accordingly, they affect the day-to-day
running of operations and business systems in contrast to strategic risks that arise from the organisation’s strategic positioning.
Operational risks are managed at risk management level (not necessarily board level) and can be managed and mitigated by
internal control systems.
The secrecy option would be a strategic risk for the following reasons.
It would radically change the environment that SHC is in by reducing competition. This would radically change SHC’s strategic
fit with its competitive environment. In particular, it would change its ‘five forces’ positioning which would change its risk
profile.
It would involve the largest investment programme in the company’s history with new debt substantially changing the
company’s financial structure and making it more vulnerable to short term liquidity problems and monetary pressure (interest
rates).
It would change the way that stakeholders view SHC, for better or worse. It is a ‘crisis issue’, certain to polarise opinion either
way.
It will change the economics of the industry thereby radically affecting future cost, revenue and profit forecasts.
There may be retaliatory behaviour by SHC’s close competitor on 25% of the market.
[Tutorial note: similar reasons if relevant and well argued will attract marks]
5 All managers need to understand the importance of motivation in the workplace.
Required:
(a) Explain the ‘content theory’ of motivation. (5 marks)
5 The way in which managers treat their employees can significantly influence the satisfaction that the employees derive from their work and thus the overall success of the organisation. Understanding the importance of motivation is therefore an important management skill.
(a) Content theories address the question ‘What are the things that motivate people?’
Content theories are also called need theories (because they concentrate on the needs fulfilled by work) and are based on the notion that all human beings have a set of needs or required outcomes, and according to this theory, these needs can be satisfied through work. The theory focuses on what arouses, maintains and regulates good, directed behaviour and what specific individual forces motivate people. However, content theories assume that everyone responds to motivating factors in the same way and that consequently there is one, best way to motivate everybody.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-10-12
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-10-12
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-08-14
- 2019-03-14
- 2019-01-05
- 2019-03-16
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-08-14
- 2019-03-14
- 2019-03-09
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-08-14
- 2019-03-16
- 2019-01-05
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-08-14