ACCA考试注意事项你都了解吗?
发布时间:2022-05-19
很多小伙伴第一次参加ACCA考试时,对于考试注意事项还不太了解。为了帮助大家,51题库考试学习网为大家带来了相关资讯,一起来看看吧!
1、ACCA考试物品准备
ACCA在国内多个城市都设有考点,为很多考生提供了便利。即便如此,考试迟到的考生依然每年都有。因此,各位考生一定要提前到达考场,切忌匆匆忙忙,保证有良好的心态参加考试。出门前,一定要检查好是否带好了ACCA准考证、身份证、黑色圆珠笔、计算器等用品。
2、考试时间管理
ACCA的考试时间非常紧张,很多人没有通过的原因就是因为没有做完试卷。所以,ACCA考试前一定要合理分配好答题时间,最好要精确到每道题目需要花费多少时间。如果一道题目超过了预期的答题时间,建议果断停笔做下一道题。
3、ACCA答题规则
ACCA考试时,先读题,先不要动笔写,先构思答题思路,然后根据问题来分配每一段要答的内容,以及答题需要花费的时间。此外,考生一定要注意答题字迹清晰,ACCA考试中有很多问答题,通常都需要考生大篇幅地书写,但是ACCA答题纸空间有限,如果字迹不清,很容易让考官找不到答案在哪里。答题过程中如果有些小点没有想起来,可以在答题纸上先留白,之后再进行补充。
4、ACCA答题思路及要点
ACCA考试最重要的一点是看到题目的时候一定要知道考官在考什么,哪块内容,哪个知识点。这样才能对应地给出考官要的点。否则,即便写了几百个字,但是没有一句话说到重点,也是白费力气。ACCA得分项里还有一个professional marks,这是考生整体答案质量的加分项,ACCA考官主要考察考生的论辩能力、逻辑思维的缜密性以及答题结构的完整性。
5、ACCA答题小技巧
在ACCA考试中,有一点原则:简单的分数一定要拿到。看到题目之后,有简单好做的题目尽量先完成,因为这些分数是很容易拿到的,也不会花费很多时间,把时间都留给难题。而且,先做简单的题目可以让你尽快进入ACCA的考试状态,降低紧张感。
如果在ACCA答题过程中发现一道题很难,一时之间无法解决,千万不要为了一棵树丢了整片森林,先去完成其他力所能及的题目。最重要的是,尽量不要留白,即便一时理不清正确的思路,也先把自己设想的答案写出来,比起答案,ACCA考官更看重考生的答题思路。
以上就是今天分享的全部内容了,各位小伙伴根据自己的情况进行查阅,希望本文对各位有所帮助,预祝各位取得满意的成绩,如需了解更多相关内容,请关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(ii) The percentage change in revenue, total costs and net assets during the year ended 31 May 2008 that
would have been required in order to have achieved a target ROI of 20% by the Beetown centre. Your
answer should consider each of these three variables in isolation. State any assumptions that you make.
(6 marks)
(ii) The ROI of Beetown is currently 13·96%. In order to obtain an ROI of 20%, operating profit would need to increase to
(20% x $3,160,000) = $632,000, based on the current level of net assets. Three alternative ways in which a target
ROI of 20% could be achieved for the Beetown centre are as follows:
(1) Attempts could be made to increase revenue by attracting more clients while keeping invested capital and operating
profit per $ of revenue constant. Revenue would have to increase to $2,361,644, assuming that the current level
of profitability is maintained and fixed costs remain unchanged. The current rate of contribution to revenue is
$2,100,000 – $567,000 = $1,533,000/$2,100,000 = 73%. Operating profit needs to increase by $191,000
in order to achieve an ROI of 20%. Therefore, revenue needs to increase by $191,000/0·73 = $261,644 =
12·46%.
(2) Attempts could be made to decrease the level of operating costs by, for example, increasing the efficiency of
maintenance operations. This would have the effect of increasing operating profit per $ of revenue. This would
require that revenue and invested capital were kept constant. Total operating costs would need to fall by $191,000
in order to obtain an ROI of 20%. This represents a percentage decrease of 191,000/1,659,000 = 11·5%. If fixed
costs were truly fixed, then variable costs would need to fall to a level of $376,000, which represents a decrease
of 33·7%.
(3) Attempts could be made to decrease the net asset base of HFG by, for example, reducing debtor balances and/or
increasing creditor balances, while keeping turnover and operating profit per $ of revenue constant. Net assets
would need to fall to a level of ($441,000/0·2) = $2,205,000, which represents a percentage decrease
amounting to $3,160,000 – $2,205,000 = 955,000/3,160,000 = 30·2%.
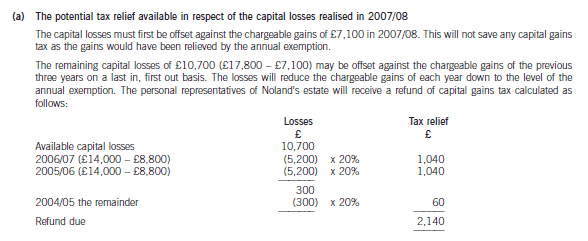
5 Crusoe has contacted you following the death of his father, Noland. Crusoe has inherited the whole of his father’s
estate and is seeking advice on his father’s capital gains tax position and the payment of inheritance tax following his
death.
The following information has been extracted from client files and from telephone conversations with Crusoe.
Noland – personal information:
– Divorcee whose only other relatives are his sister, Avril, and two grandchildren.
– Died suddenly on 1 October 2007 without having made a will.
– Under the laws of intestacy, the whole of his estate passes to Crusoe.
Noland – income tax and capital gains tax:
– Has been a basic rate taxpayer since the tax year 2000/01.
– Sales of quoted shares resulted in:
– Chargeable gains of £7,100 and allowable losses of £17,800 in the tax year 2007/08.
– Chargeable gains of approximately £14,000 each tax year from 2000/01 to 2006/07.
– None of the shares were held for long enough to qualify for taper relief.
Noland – gifts made during lifetime:
– On 1 December 1999 Noland gave his house to Crusoe.
– Crusoe has allowed Noland to continue living in the house and has charged him rent of £120 per month
since 1 December 1999. The market rent for the house would be £740 per month.
– The house was worth £240,000 at the time of the gift and £310,000 on 1 October 2007.
– On 1 November 2004 Noland transferred quoted shares worth £232,000 to a discretionary trust for the benefit
of his grandchildren.
Noland – probate values of assets held at death: £
– Portfolio of quoted shares 370,000
Shares in Kurb Ltd 38,400
Chattels and cash 22,300
Domestic liabilities including income tax payable (1,900)
– It should be assumed that these values will not change for the foreseeable future.
Kurb Ltd:
– Unquoted trading company
– Noland purchased the shares on 1 December 2005.
Crusoe:
– Long-standing personal tax client of your firm.
– Married with two young children.
– Successful investment banker with very high net worth.
– Intends to gift the portfolio of quoted shares inherited from Noland to his aunt, Avril, who has very little personal
wealth.
Required:
(a) Prepare explanatory notes together with relevant supporting calculations in order to quantify the tax relief
potentially available in respect of Noland’s capital losses realised in 2007/08. (4 marks)
(c) In the context of a standard unmodified audit report, describe the content of a liability disclaimer paragraph,
and discuss the main arguments for and against the use of a liability disclaimer paragraph. (5 marks)
(c) It has become increasingly common for audit firms to include a disclaimer paragraph within the audit report. However, it is
not a requirement of auditing standards and individual audit firms need to assess the advantages and disadvantages of the
use of a disclaimer paragraph.
The wording is used to state the fact that the auditor’s report is intended solely for the use of the company’s members as a
body, and that no responsibility is accepted or assumed to anyone other than the company and the company’s members as
a body.
The main perceived advantage is that the disclaimer should help to reduce the exposure of the audit firm to liability claims
from anyone other than the company or the company’s body of shareholders. The disclaimer makes it clear that the audit
firm reports only to those who appointed the firm, i.e. the members of the company, and this may make it more difficult for
the audit firm to be sued by a third party.
It is also argued that the use of a disclaimer could help to bridge the ‘expectation gap’ by providing a clearer indication of the
responsibility of the auditor.
In this way the audit firm can manage its risk exposure in an increasingly litigious environment. Recent high profile legal cases
against audit firms, such as the Bannerman case in Scotland, illustrate that an audit firm’s duty of care can extend beyond
the company and its shareholders, and that audit firms should consider how to protect themselves against liability claims.
Tutorial note: It is appropriate here to quote recent cases such as the Bannerman case to illustrate the reason why audit
firms face increased potential exposure to claims from third parties. However, knowledge of specific legal cases is not
required to gain full marks for this requirement.
However, it can be argued that a disclaimer does not necessarily work to protect an audit firm. Each legal case has individual
circumstances, and while a disclaimer might protect the audit firm in one situation, equally it may not offer any protection
where the facts of the case are different.
In addition, it is often argued that if an audit firm conducts an audit using full due care and diligence, there is no need for a
disclaimer, as a high quality audit would be very unlikely to lead to any claims against the audit firm. Consequently, it could
be argued that the use of disclaimers as a means to limit liability could permit low quality audits to be performed, the auditors
being confident that legal cases against them are restricted due to the presence of a disclaimer within the audit report.
2 (a) Explain the term ‘backflush accounting’ and the circumstances in which its use would be appropriate.
(6 marks)
(a) Backflush accounting focuses upon output of an organisation and then works backwards when allocating costs between cost
of goods sold and inventories. It can be argued that backflush accounting simplifies costing since it ignores both labour
variances and work-in-progress. Whilst in a perfect just-in-time environment there would be no work-in-progress at all, there
will in practice be a small amount of work-in-progress in the system at any point in time. This amount, however, is likely to
be negligible in quantity and therefore not significant in terms of value. Thus, a backflush accounting system simplifies the
accounting records by avoiding the need to follow the movement of materials and work-in-progress through the manufacturing
process within the organisation.
The backflush accounting system is likely to involve the maintenance of a raw materials and work-in–progress account
together with a finished goods account. The use of standard costs and variances is likely to be incorporated into the
accounting entries. Transfers from raw materials and work-in-progress account to finished goods (or cost of sales) will probably
be made at standard cost. The difference between the actual inputs and the standard charges from the raw materials and
work-in-progress account will be recorded as a residual variance, which will be recorded in the profit and loss account. Thus,
it is essential that standard costs are a good surrogate for actual costs if large variances are to be avoided. Backflush
accounting is ideally suited to a just-in-time philosophy and is employed where the overall cycle time is relatively short and
inventory levels are low. Naturally, management will still be eager to ascertain the cause of any variances that arise from the
inefficient usage of materials, labour and overhead. However investigations are far more likely to be undertaken using nonfinancial
performance indicators as opposed to detailed cost variances.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-08-15
- 2022-05-20
- 2021-05-29
- 2021-05-29
- 2019-01-04
- 2021-05-29
- 2020-10-21
- 2020-09-05
- 2021-02-13
- 2020-10-10
- 2019-12-29
- 2020-10-10
- 2020-10-18
- 2020-10-21
- 2021-02-13
- 2020-10-10
- 2020-10-21
- 2021-02-13
- 2021-02-13
- 2021-02-21
- 2021-02-21
- 2020-10-21
- 2022-05-18
- 2019-03-29
- 2022-05-22
- 2021-05-29
- 2022-05-21
- 2022-03-05
- 2020-09-05
- 2021-05-29